“No Possible Escape”: A Short History of Fire at the Huron Gaol
“No Possible Escape” sounds positive when it comes to jailbreaks, but less so in the case of emergency. Curator of Engagement & Dialogue Sinead Cox looks back at fire and fire safety at the Huron Historic Gaol.
The Huron Historic Gaol is one of the most recognizable, historically significant and architecturally unique buildings in Huron County. Today it stands as a venue for visitors to hear the stories of the prisoners and staff who walked its halls, and considering the number of times the building has caught fire over its 180+ year history, this is nothing less than a small miracle.
Although the outer walls may give the impression that it is solid stone, the construction of the gaol interior is actually significantly timber. The unique octagonal layout of rooms and yards around a central spiral staircase are designed to keep prisoners in, with perhaps less architectural forethought when it comes to allowing people to quickly get out, should the upper floors become engulfed in flames.
In 1851, when the building was only a decade old and served the United Counties of Huron, Perth and Bruce, an errant chimney spark caused the first known fire of significance. Fortunately, the only harm sustained in that instance was damage to the building’s roof. Afterwards, the Gaol Inspector recommended covering the roof with metal, and that the county purchase a new ladder tall enough to actually enable water to be carried high enough to fight a fire (staff presumably having discovered the inadequacies of the previous ladder during the emergency). No ladder would have been very useful as a means of rescue for prisoners, however, as all of the windows on the gaol’s upper floors were barred to prevent escape.
In the 1860s the County of Huron replaced the tin-covered roof with slate, later swapped for asphalt shingles about a century later. When reverting to slate in 2021, roofers discovered lumber inside the cupola still bore blackened scorch marks from historic fires. The cupola, or central tower, has been struck by lightning at least twice: in 1892 and 1929. Torrential rain prevented fire in the first case, but the second strike “set the tower ablaze” just after one a.m. According to The Clinton News Record, “a terrific electric storm was in progress and firemen had difficulty at first in plying streams of water on the tower, owing to its height. Some of the firemen climbed on to the slate roof, slippery with rain, and fought the flames from perilous positions.” The newspaper claimed that despite the late hour and extreme weather, a crowd of people gathered outside the gaol’s walls to watch their efforts. While firefighters risked their lives to stop the fire from spreading to the lower floors, a constable escorted the seven prisoners currently committed to the Huron Gaol to an outside courtyard, still confined within the 18 ft walls. Thankfully, the fire was successfully contained within the cupola and extinguished, but the flames and the water employed to douse them had caused more than $1,000 in damages (equal to just over $16,500 today). The county enlisted prisoner labour to help with the subsequent clean-up and repairs.

Fire bucket. M951.0732.001


Huron Historic Gaol, Goderich Ontario

1855 Fireman’s helmet donated by Town of Goderich. M951.0734.001.
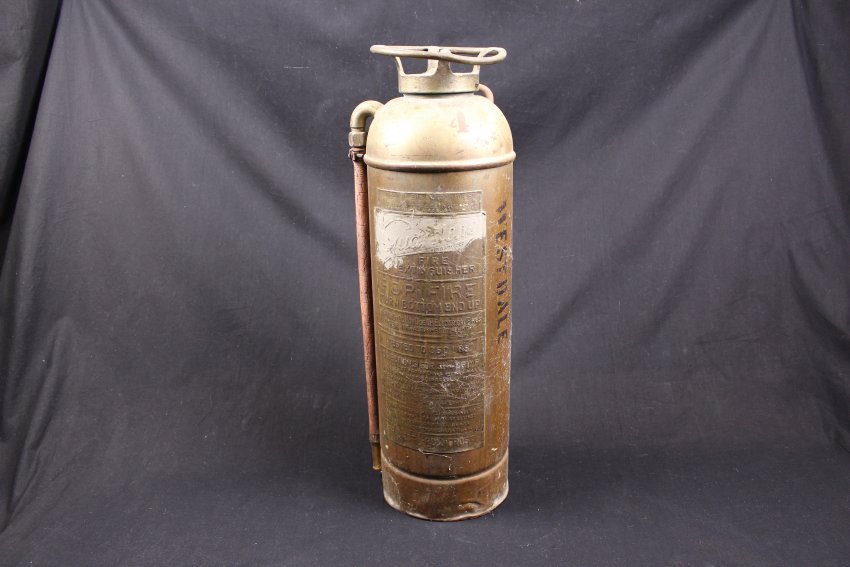

Fire Extinguisher. 2017.0024.003.

A950.1976.001. Fire crew at former Goderich Fire Station located on East Street, 1925.
The cupola caught fire again in 1944, this time from burning leaves, either carried from the ground by a strong wind or ignited in the eaves by a spark. Although this fire burned only briefly, it caused destruction and water damage similar or worse than the 1929 blaze: costs duly submitted to the county’s insurer.
Officials and staff recognized the inadequacies of the gaol’s design very early in its operation: the lack of fire exits was one of the reasons that District Council and the courts complained about meeting there before the construction of a separate courthouse in 1856. Despite the general awareness of the threat, safety measures provided by the county did not always meet the needs of staff or emergency responders. After the 1892 lightning strike, Gaoler William Dickson found that the gaol’s fire hose was faulty, and burst in multiple places when tested with pressure. As early as 1882, after yet another recent narrow escape from flames, local newspaper editorials from the Goderich Star and Clinton New Era condemned the gaol as an outdated fire trap. The Era argued for replacing the gaol and courthouse with new, modern municipal buildings in a more central location. The Gaol and Court House Committee instead recommended “that a Babcock Fire Extinguisher for the gaol be furnished, also that a suitable water tank be built in the gaol yard, owing to the inflammable and unsafe condition of the gaol stairs, there is no possible escape for the inmates in case of fire.”
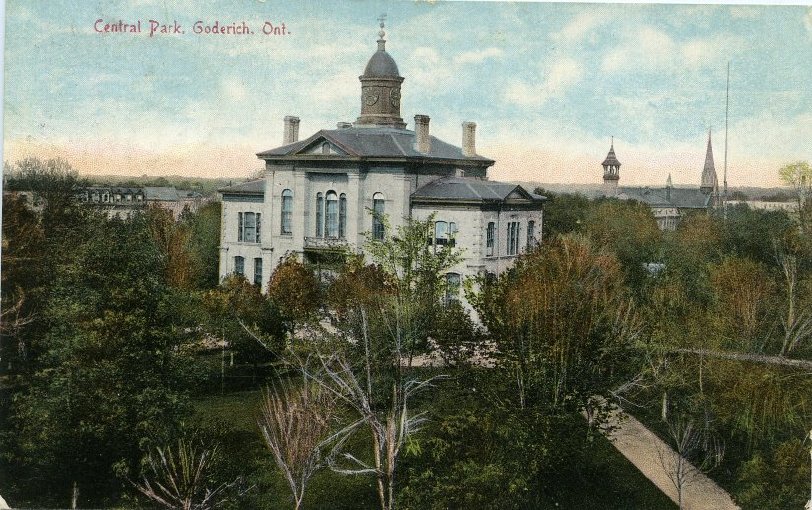

Postcard of courthouse at “Central Park” or Square, Goderich. Built 1856. This courthouse was destroyed by fire and replaced in 1954. 2008.0032.083.
In the 1890s, Huron County Council acknowledged the aging heating stoves in each cell block’s dayroom as another serious danger and replaced them. Prior to electric lights, staff also had to contend with mandatory corridor lamps, burning day and night at the risk of overheating. Gaoler Dickson lamented to County Council in 1896 that, “twice [a lamp has exploded] during the almost 32 years I have been in your employ. The last time it was towards morning and fortunately my subordinate was awake and succeeded in extinguishing the fire at the cost of the bedding of two beds.” Dickson credited the turnkey’s quick action in preventing what was nearly a terrible tragedy: “At the time of the explosion there were 18 prisoners under lock and key, besides 5 members of my own family who were sleeping on the second floor. Had the flames caught the stair, all on the upper floors would have been entirely cut off from escape. In view of this danger to life and property, I would respectfully ask that you place one incandescent in said hallway.” The gaoler’s lobbying successfully resulted in the installation of incandescent lights at the gaol, but the issue of the single exit remained unaddressed. It’s easy to imagine that if the fire had spread beyond the smothering power of gaol blankets, that a quick decision may have been made to prioritize the evacuation staff and family before the overcrowded inmates sleeping behind multiple locked doors.
The close-call fires at the gaol over the decades were all seemingly accidental, with the exception of one incident during the holiday season in 1943. The gaol’s annual Christmas celebrations included a special meal for the prisoners with treats donated by the community, and that year they also enjoyed a decorated Christmas tree. On December 27th, the dry boughs of the tree caught fire in one of the cell blocks, spreading to the woodwork and choking that ward with thick smoke. The Goderich fire department responded to gaol staff’s call for help, and successfully extinguished the flames in a manner of minutes. A follow-up investigation found that the cell block’s three resident inmates had intentionally started the fire to create a distraction for escape. Convicted forger Floyd McCullough admitted to helping his teenaged cellmates, Angus Trudeau and Lorne Derevere, in devising how to ignite the Christmas tree remnants. The two younger men, committed for robbing Bayfield-area cottages, ultimately also pled guilty to the arson. No opportunity for jailbreak had ever actually materialized as planned; the trio were simply evacuated to another part of the gaol to avoid the smoke inhalation that may have endangered their lives if not for a turnkey’s quick arrival on the scene. All three faced added time behind bars for the conspiracy.

The aging building’s vulnerability to fire remained a concern throughout the twentieth century, resulting in a fire-proof coating applied to the cells in 1939, various furnace installations and upgrades, and an alarm system installed by the 1950s. Jurisdiction over Ontario’s county correctional facilities transferred to the Province in 1964, and in 1972 the Ontario Department of Correctional Services decided to close the Huron Gaol. From 1974, the gaol opened its doors as a historic site and museum, originally managed by the Historic Jail Board– the County of Huron retained responsibility for fire insurance. The County resumed direct control of the building in the 1990s.
The Huron Historic Gaol would pass its 175th birthday before finally gaining a fire escape and new fire exits on the second and third floors of the gaol after major upgrades in 2018. The work was undertaken with care to protect the site’s historical appearance and architecture. As a historic site, fire safety could be addressed to meet contemporary standards without concerns about compromising security. Today, the spectre of potential disaster by fire need not haunt staff and visitors to the degree it once did generations of prisoners and gaol employees. The gaol’s countless near misses with destruction are a reminder of the importance of adequate preparations and equipment to combat fire, as well as the need for strict safety regulations for public buildings. It is only a mixture of ad hoc precautions, the quick actions of the gaol’s small staff, the intervention of local firefighters and also simple luck, that has successfully preserved this one-of-a-kind building and the lives of those who have lived and worked within its walls over three separate centuries.
Find out More!
- The actions of the Save the Jail Committee also directly saved the gaol from destruction! Read more in The Save the Jail Society: How the Huron Historic Gaol Dodged Demolition by Kyra Lewis.
- What inspired the gaol architecture? Read more in this blog post by Kyra Lewis about the construction of the gaol and its Panopticon design.
- This blog post was researched using the County of Huron’s historical digitized newspapers and council minutes held at the Huron County Archives.