
by Sinead Cox | Aug 25, 2020 | Archives, Blog, Exhibits, Image highlights, Investigating Huron County History
In anticipation of the Huron County Museum’s in-development exhibit Forgotten: People & Portraits of the County, volunteer Kevin den Dunnen takes an in-depth look at one of the many studio photographers to work in Huron County, and traces the professional and personal journey of Irene Burgess.

Summer of 1923 “old home week” in Mitchell, Ontario. Irene is the farthest left of the four. Image courtesy of the Stratford-Perth Archives.
Hiding within the Huron County Museum’s online and free-to-use newspaper archives are an unlimited number of stories like the one of Miss Irene Burgess. Irene Burgess was a woman that defied societal norms. In a time where women were rarely given the freedom to pursue a chosen career, Irene managed her own photography studio. While many women were expected to marry and have families, Irene stayed single. She was also faced with many tragedies in her life. Neither of her two siblings lived past 32. Her mother passed away at 51. Her niece nearly died at the age of 6. She lost the photography studio after an explosion. Through all of this, the communities of Perth and Huron Counties rose to support her.
Personal Life
Nettie Irene Burgess was born September 20, 1901, in Mitchell, Ontario. Her parents were Nettie and Walter Burgess. She had two siblings – an older sister named Muriel, born in 1896, and a younger brother named Macklin, born in 1912. Her father, Walter, was a long-time photographer in Mitchell and owner of W.W. Burgess Studio. Growing up around photography gave Irene plenty of exposure to the business. This experience would prove to be important in her adult life.
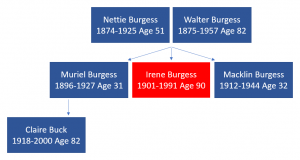
A brief family tree of the Burgess family. Of note, it only contains the names of family members included in this article.

Excerpt from the November 26, 1925, edition of The Clinton News-Record detailing the passing of Irene’s mother Mrs. Nettie Burgess.
Irene experienced several tragedies throughout her life. By her 43rd birthday, only she and her father survived from their family of five. The first to pass was Irene’s mother, Nettie Helena Burgess, on November 22, 1925, at the age of 51. Irene’s sister, Mrs. D.F. Buck ( née Muriel Burgess) and her 6-year-old daughter Claire had been staying with her parents Walter and Nettie Burgess; Mrs. Buck had been ill for some time. During their stay, Claire became ill with pleuro-pneumonia. On the brink of death for several days, she began to recover with the help of her grandmother, Nettie. While caring for Claire, Nettie contracted pneumonia. Less than six days later, Nettie passed away in the presence of her family and nurse. 6-year-old Claire would live for another 75 years thanks to the care of her grandmother.
The next member of Irene’s family to pass would be her sister Muriel. Muriel was married to D.F. Buck, a photographer from Seaforth. They had three children, a daughter named Claire, and two sons named Craig and Keith. On March 24, 1926, an update in the Mitchell Advocate indicated that Irene would be visiting her sister, Mrs. D.F. Buck, at the Byron Sanitorium. According to the update, Mrs. Buck was “progressing favourably” but had been in poor health for some time. Almost fourteen months later on May 12, 1927, The Seaforth News wrote about the death of Mrs. D. F. Buck occurring the past Friday. While not mentioning the cause, the obituary described her as being “in poor health for a considerable period.”
On July 18, 1944, the Clinton News Record posted an obituary for Irene’s brother Macklin Burgess who passed away from a long-time illness at the age of 32. Macklin was in the photography and radio business. He left behind his wife, Elizabeth May, and three children, David, Nancy, and Dixie.
The next of Irene’s family to pass would be her father, Walter Burgess, in 1957 at the age of 82.
An interesting note in the life of Miss Irene Burgess is that she never married. In the Dominion Franchise Act List of Electors, 1935, Irene (age 34) is listed as a spinster (meaning a woman that is unmarried past the age considered typical for marriage). Whenever Irene is referenced in a newspaper, her title is Miss Irene Burgess. Irene would live until 1991.
The Clinton Studio

A notice posted by Walter Burgess in the May 23, 1929, edition of The Clinton News-Record
Walter Burgess operated a Clinton studio throughout the 1920s. The November 26th, 1925 edition of The Clinton News-Record mentions that Walter had only been spending one day a week at his Clinton Studio being “short of help.” A notice posted in The Clinton News-Record on May 23 1929 by Walter Burgess stated that his Clinton studio would only be open “the second and last Tuesdays in each month.” On October 1 of 1931, Walter announced that his newly-renovated Clinton studio would be open every weekday. His daughter, Miss Irene Burgess, would now be in charge of the location. Walter proclaimed Irene as “well experienced in Photography” and having “long experience with her father.” Not long after Irene became manager, Clinton residents would see the name Burgess Studios much more often in their newspapers.
When Irene began managing the Clinton Studio in 1931, advertisements for the business began increasing. The slogan “Photographs of Distinction” appeared in advertisements from 1937 until the week of the fire. These ads were brief, only including the business name, slogan, Irene’s name, and the services provided. Earlier advertisements include one from 1933: “It is your duty to have a good photograph. Your family wants it – business often demands it.” Another example from 1932 reads, “You have plenty of leisure time to get that portrait of [the] family group taken.” The Clinton studio began under the leadership of Walter W. Burgess, but Irene would soon grow the business larger than her father had the time for– that is, until the explosion.

Advertisement posted in the January 26, 1933, edition of The Clinton News-Record.
The Explosion
On the afternoon of Monday, November 24, 1941, an explosion set fire to the second story of the J. E. Hovey Drug Store sweeping the entire business block. This was the place of business for Burgess Studio, Clinton. The fire swept through the building and damaged several businesses including R. H. Johnson Jewelry Store, Charles Lockwood Barber Shop, and Mrs. A MacDonald’s Millinery and Ladies Wear Shop. Irene was not in the studio when the fire started and did not call the authorities. Instead, the fire was discovered by Police Constable Elliot who identified smoke around the second-story window of the J. E. Hovey Drug Store Building. The fire was well covered in local newspapers. Featured on the second page of the Seaforth News more than a week after the incident, it was reported that the fire almost reached the “main business section of the town.” On its front page the week of the accident, The Clinton News-Record described the fire as “one of the most dangerous Clinton firemen have fought for years.” Unfortunately, Irene did not have insurance and was forced to close her business in Clinton. An update written on November 27, 1941 in The Clinton News-Record mentioned Irene’s departure for Mitchell to stay with her father for an “indefinite time.” A week later, on December 4, 1941, Irene posted a notice in the News-Record reading that, “owing to the recent fire damaging my equipment and Studio, I will be unable to continue operation.” She suggested that customers could mail their orders to the new studio. Additionally, customers could drive to her father’s studio in Mitchell and have their travel expenses paid. While this time must have been devastating for Irene, the community came together to show their support for her.
Community Support

Excerpt from the December 12, 1941, edition of the Huron Expositor describing an even held in Irene Burgess’ honour.
Two weeks after the explosion, the Mitchell Advocate reported about an event held at the I.O.O.F. Hall where Irene was the “honoured guest.” The event was planned by Irene’s friends Mrs. Dalton Davidson, Mrs. Earl Brown, Mrs. Harold Stoneman, and Miss Florence Paulen. Entertainment included skits, piano music by Mrs. A. Whitney, cards, and a “bountiful lunch.” Irene received a “purse of money” and personal gifts from her friends along with their condolences. The rallying support for Irene shows the positive impact she had in the communities of Clinton, Seaforth, and Mitchell. An uplifting end to an otherwise sad story.
Conclusion
Aside from her brother’s passing in 1944, Miss Irene Burgess was seemingly never mentioned again in the Huron County Newspapers accessible through the digital newspaper portal. She would live until 1991 in St. Marys, Ontario.
Huron County’s digitized newspaper collection is a vast historical database where you can find historical stories from our own county. While performing research for the upcoming exhibit “Forgotten: People & Portraits of the County,” I came across this story which piqued my interest. Without access to the digitized newspaper collection, the story of Irene’s remarkable journey would never have been found. This post was compiled using newspaper articles between the years of 1925 and 1944. Birth and death dates were found within newspapers and using external resources.
If you have a photograph by a Huron County photographer you would like to donate or share, please contact the Museum’s archivist by calling 519-524-2686, ext. 2201 or email mmolnar@huroncounty.ca. To learn more about the Huron County Archives & Reading Room, visit: https://www.huroncountymuseum.ca/huron-county-archives/
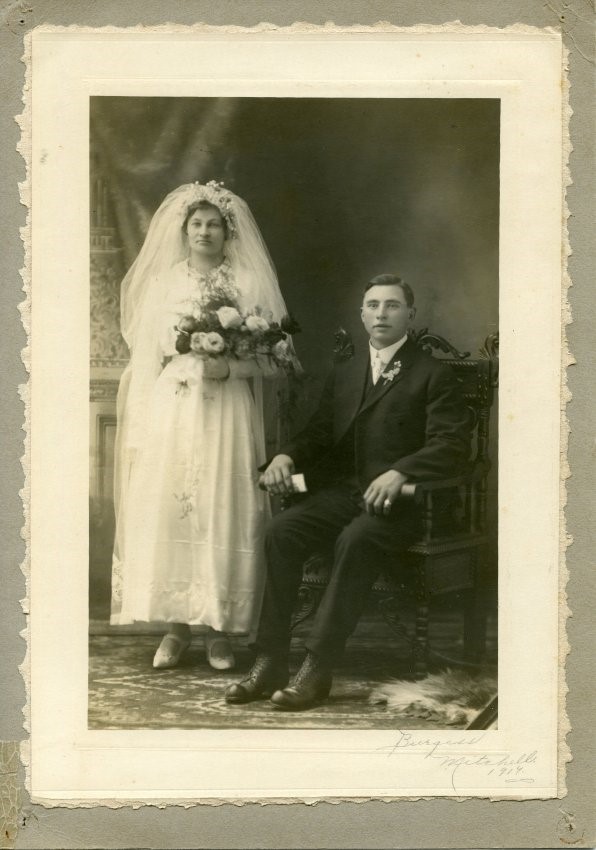

A950.1857.001 A photograph taken by Burgess Studio Mitchell in 1914. If you have a photograph from Burgess’ Studio, Clinton you would like to donate, please consider contacting the Huron County Museum.

by Sinead Cox | Jun 4, 2020 | Investigating Huron County History
Curator of Engagement and Dialogue Sinead Cox shares the story of a historical quarantine in the summer of 1916.
Although you may have heard (to the point of cliché) that we are living in ‘unprecedented times’ during today’s COVID-19 pandemic, communities across Huron County have seen quarantines and the temporary closure of schools and businesses before. Although usually on a much smaller and localized scale, these actions in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries were in response to contagious illnesses that included influenza, measles, diphtheria, scarlet fever, smallpox, whooping cough and typhoid among others.

From The Brussels Post, July 27th, 1916.
In 1916 an outbreak of infantile paralysis (polio or poliomyelitis) hit North America. The poliovirus is most dangerous to children under five years of age and in serious cases can cause permanent and debilitating nerve and muscle damage to survivors if non-fatal. The 1916 epidemic was particularly devastating in New York and then appeared in Canadian cities like Montreal before eventually arriving in southern Ontario. In Ontario, the provincial Medical Board of Health enacted quarantine regulations and required doctors to report all cases or face prosecution.
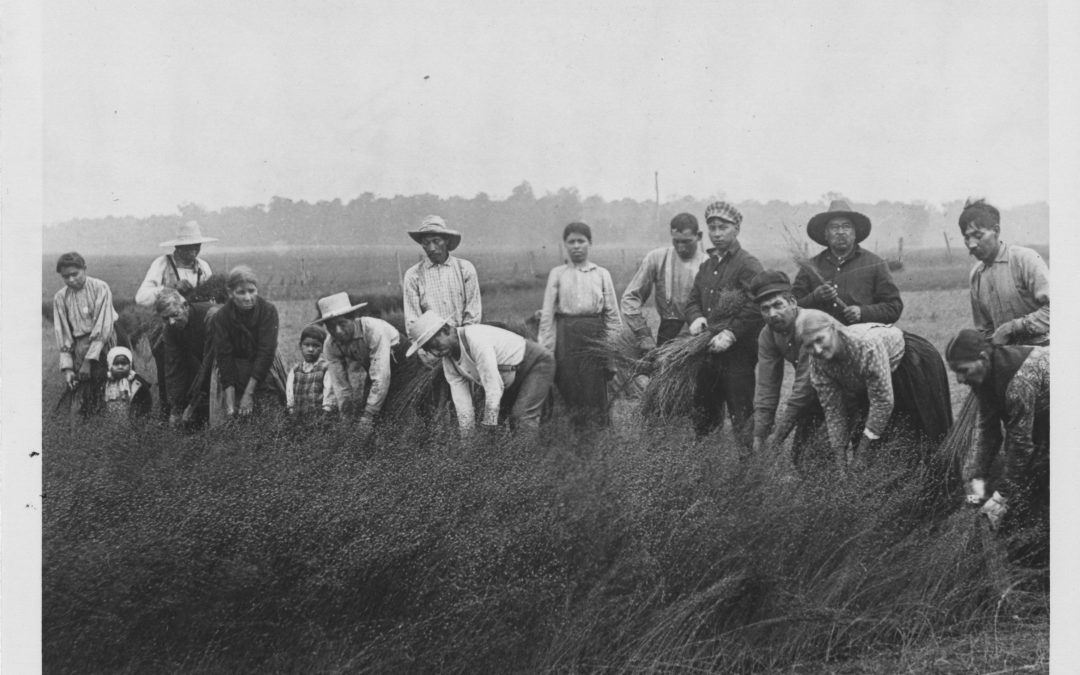
The outbreak had reached Huron County by July, when a fourteen-month-old girl in Varna died: only the second fatal case confirmed in Ontario up to that point. Panic hit the next month when three young children in Hullett Township contracted the much-feared disease. The children had come to live temporarily in Hullett (now part of the Municipality of Central Huron) with their parents during the flax harvest, but their permanent home was reported as ‘Muncey Reserve.’ Indigenous families from Southwestern Ontario reserve communities, including those on the shore of the Thames River south of London and also Saugeen First Nation to the north, were a crucial labour force for annual flax harvests in the early twentieth century. Entire families moved seasonally to pull flax for Huron growers; they worked and lived in close contact with each other, camping alongside their worksites.
The sick children belonged to a group of about 15 families living in tents roughly six miles from Clinton when the infantile paralysis struck-eventually infecting two five-year-olds and a two-year-old. A local Blyth doctor treated the first cases and told the area newspapers that the farm workers’ living situation presented a challenge for protecting the lives of the other 23 children in the camp: “Isolation and quarantine, so necessary for the treatment of infantile paralysis, are something hard to enforce in any Indian reservation or encampment…We are doing what we can to prevent any spread of the disease, and watching for further symptoms, but it is next to impossible to enforce the requisite isolation.” The vast majority of poliovirus cases are completely asymptomatic. The disease can spread through direct contact or via contamination by human waste.

From the Wingham Advance, August 31st, 1916.
For one of the five-year-olds, the virus was tragically fatal on August 25th, but the other two children soon appeared to be recovering. Local newspapers did not identify any of the camp members by name, but a death registration reveals that the little girl who lost her life was Annie Corneolus, the five-year-old daughter of Abram and Elizabeth. She was ill only one day, but the polio had caused lethal ‘paralysis of respiration.’ Her birthplace is recorded as Oneida Reserve (Oneida Nation of the Thames). Annie’s burial took place at Burns Cemetery, Hullett. Local health officials separated the families with sick children from the rest of their neighbours and they proceeded to quarantine at a farmer’s house on the 11th Concession. School Section # 11 at Londesborough cancelled classes for all students as a precaution.
Fortunately, their quarantine appeared successful and there were no further cases reported. The Clinton New Era announced that “the infantile paralysis scare in Hullett Township has pretty well blown over.” When health authorities lifted quarantine the families impacted returned to their reserve community, and the rest of the camp moved on to Blyth to continue their flax-pulling work. The Huron newspapers make no mention of whether or not the surviving children suffered any long-term health effects. Later reports listed the total number of province-wide infantile paralysis cases at 64 for July and August of 1916, with 8 resulting deaths–meaning that 25% of those total polio deaths occurred in Huron County.

From the Signal (Goderich), July 20th, 1916.
There is no cure for polio, but the Salk vaccine of 1955 would eventually be effective and widely used to prevent the disease; after continuous deadly outbreaks throughout the first half of the twentieth century, childhood vaccinations have eradicated polio in Canada.
The living and working conditions of temporary farm workers in 1916 would have made following advice about precautionary hygiene and social distancing almost impossible to follow-and many people in Canada are facing those same challenges today, without equal housing or opportunities to practice self-isolation under novel coronavirus. Although the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic is not the same as polio, the reality that Indigenous communities continue to be disproportionately impacted by pandemics, and that temporary and migrant workers are at a higher risk because of a lack of resources and opportunities to safely distance is absolutely precedented.
More Info about the history of polio in Canada: https://www.cpha.ca/story-polio
*Note: I wrote this blog post using contemporary newspaper accounts including the Wingham Times, The Wingham Advance, The Lucknow Sentinel, The Clinton New Era, The Clinton News-Record, the Signal (Goderich) and others, all accessed from Huron’s free historical newspaper database: https://www.huroncountymuseum.ca/digitized-newspapers/ Annie’s death documentation was accessed via Ancestry.ca (Archives of Ontario; Toronto, Ontario, Canada; Collection: MS935; Reel: 220). All of these accounts were written from a settler point of view (as is my own), and the newspapers did not include the voices or even the names of the community members impacted. If you have any further information you’d like to share about this outbreak or similar outbreaks in the past contact museum@huroncounty.ca.

by Sinead Cox | May 16, 2020 | Collection highlights, Exhibits, For Teachers and Students, Huron Historic Gaol, Uncategorized
Looking for a way to remotely visit the Huron County Museum or the Historic Gaol with your family or class? Here are some activities you can try using our virtual resources! Have questions about what you see and how it was used? Email museum@huroncounty.ca to talk to an expert!
HURON COUNTY MAIN STREET at the Huron County Museum
Click to visit our virtual exhibits, including Huron County Main Street! Can you find everything? Pick a favourite object that isn’t on the list, and ask others to find it!
360 TOUR at the Huron Historic Gaol
Go to the Huron Historic Gaol’s page and scroll to the bottom to find our 360 degree tour! Use the arrows and Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 buttons to explore in all directions. Keep clicking to go inside the rooms, including a cell block. Found everything on the list? Play I spy with my little eye!


by Sinead Cox | May 15, 2020 | Huron Historic Gaol, Investigating Huron County History
In this two-part series, Curator of Engagement & Dialogue Sinead Cox illuminates how the Second World War entered the walls of the Huron Historic Gaol. Click here for Part One: The ‘Defence of Canada’ in Huron County.
In the summer of 1940, when the Netherlands fell to Nazi Germany, a ripple effect extending to the Great Lakes would unexpectedly commit thirteen “alien seamen” to the Huron Jail.*
At the outset of the Second World War in 1939, the Oranje Line, also known in Dutch as Maatschappij Zeetransport N.V, was a relatively new Dutch-owned transport company that serviced Great Lakes routes. The Line had only commenced operations in 1937, and its fifth vessel in the Great Lakes, the 2,800 ton diesel freighter Prins Willem III was the first deep sea motor ship to come inland; she embarked on her maiden voyage in September, 1939.
On May 9th, 1940 the Prins Willem III departed neutral Antwerp, Belgium on a routine commercial journey under Captain W. P. C. Helsdingen. In the course of one day, the ship’s professional routine would be abruptly shattered. The Prins Willem III was off the coast of Flushing when a German bomb hit the water about 200 yards from the ship and caused a huge explosion and towering pillar of water. Germany had invaded the Netherlands. Planes were flying high and out of sight, but the crew could hear the whining sound of bombs as they fell nearby. Targeted by a machine gun onslaught from Nazi fighter planes, the ship escaped via the English channel. After narrowly surviving with their lives and the boat intact to reach England, the Dutch crew would soon learn that the formerly neutral Netherlands had capitulated and their home country was now occupied by Nazi Germany.
The ship continued on its planned journey to North American waters, docking at Montreal, Duluth, Milwaukee and finally Chicago on June 25th , successfully delivering a cargo of seeds and twine. At Chicago, the crew awaited orders regarding their next destination. Meanwhile, members of the Dutch government, including Queen Wilhelmina, had fled to London, England. The government in exile required all Dutch merchant vessels abroad to now sail under the British Merchant marines, and to report to an allied port to join the war effort: which could include transporting provisions or armaments. Canada being the closest allied country, the Netherlands Shipping Commission ordered the Prins Willem III to return to Montreal and “then embark for some unnamed foreign port,” according to the Chicago Daily Tribune. 17 out of the 19 crew members refused the orders.
The crew’s actions seemed to defy easy categorization as conscientious objection or mutiny. Captain Helsdingen assured the Chicago press that the men were neither striking, mutinous, nor even refusing to do their assigned jobs aboard the ship, but the crew would not leave the neutral waters of the United States (which would not enter the war until after the bombing of Pearl Harbor in December, 1941). After their ordeal at the mercy of German bombs and guns, reluctance to return to a war zone aboard a ship that was not armed, and would not be provided an armed convoy, is hardly surprising. The Tribune quoted the crew as telling the captain, “If we cannot have weapons, we would rather spend our time in a United States jail than on the ocean.” They also feared for their families in a Nazi-occupied country and whether there could be reprisals against them—extending to arrests and transportation to concentration camps—for helping the allied cause by transporting munitions. According to the captain, the crew of the Prins Willem III feared Germany more than England.
The crew’s ‘sitdown strike’ left Commonwealth, Dutch and American authorities with no easy solutions. The standstill left most of the crew trapped on the ship, with only Captain Helsdingen legally permitted to go ashore. The crewmembers had no immigration documents to legally enter the United States, and because of the ongoing occupation of the Netherlands, the U.S. would not have been easily able to deport the sailors: thus Immigration authorities and the Coast Guard kept a close watch on the ship. The Captain could not take on an American crew to move the ship because of U.S. neutrality, and thus the Prins Willem III remained anchored unmoving at Navy Pier.
American newspaper reports emphasize that, rather than any assumed violent mutiny, the crewmembers were largely friendly and cheerful in their refusal to budge. During their months of isolation on board, the crew busied themselves cleaning, stripping and painting the masts, booms and deck, oiling “everything in sight, from door handles to winches,” and polishing every “spot of brass on the boat to glisten.” The Tribune declared when it finally left Navy Pier the Prins Willem III would probably be “the best painted, best oiled and best polished ship that ever left this port.” By September the crew’s plight had gained the sympathies of Dutch Chicagoans, who organized a committee to deliver care packages to the crew from pleasure boats.
The Dutch government-in-exile, the Oranje Line and Canadian authorities finally devised a solution in October: the Prins Willem III would take on a Canadian crew recruited from Montreal. Ten private police from the Pinkerton Detective Agency in the United States were hired to come aboard the ship with the fourteen Canadian crew-members to prevent resistance or sabotage, and the ship was escorted by the U.S. Coast Guard during its departure from Chicago. There was ultimately no violence from the crew confined below deck; according to Time Magazine, “internment in Canada looked better to the bored, sequestered Dutch than gazing at the Chicago skyline all day.” Their initial stop according to the American reports was to be an “unannounced Canadian destination,” later specified as an “Ontario Port.” That port was Goderich.

Ships in Goderich harbour, date unknown Photographer: Reuben R. Sallows (1855 – 1937)
On October 16th, 1940 the Prins Willem III—presumably painted, oiled and polished to perfection—arrived in the Goderich harbour. The secrecy surrounding the chosen port for the uncooperative crew’s disembarkment meant local customs workers were completely surprised by the ship’s unscheduled arrival, and began a tentative dialogue with Captain Helsdingen regarding next steps while further instructions from Ottawa were awaited. Again, the original crewmembers of the Prins Willem III were stuck in limbo on board, and again they made the most of it: according to the Clinton News-Record they came on deck “under the watchful eye of two [Pinkerton] detectives…getting great enjoyment out of perch fishing from the stern of the ship while they whistled modern American airs.” A local crowd of curious onlookers gathered at the harbour to gawk at the ship from a distance, and a host of exaggerated rumors quickly travelled throughout the community, including that the crew were held in irons and guarded by machine gun-wielding “G-men.”
Three days later, thirteen crew members quietly disembarked from the ship during the night, escorted by the RCMP in batches of no more than two men at a time.** Police vehicles delivered these men to the Huron Jail. The remaining crew changed their minds and agreed to sail with Captain Helsdingen and the Canadians. The Prins Willem III had vanished from the Goderich harbour by the next morning, and the Pinkerton Detectives caught a train back to Chicago.

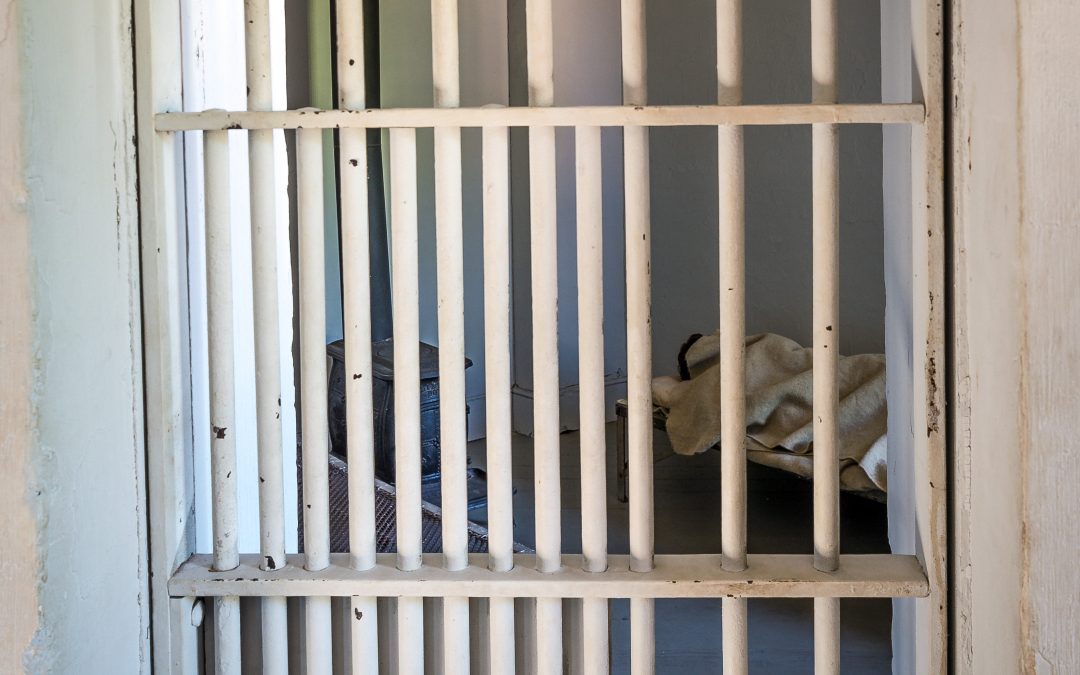
Cell in the Huron Historic Gaol.
The crew’s confines on land might have been somewhat tighter and less comfortable than their previous situation on board the Prins Willem III. Detailed inmate records are not accessible from the 1940s, but regardless of how many prisoners were already ‘guests of the county’ at the time, the arrival of thirteen ‘alien seamen’ would have left the Huron Jail, which has only twelve cells, over-capacity and somewhat crowded. The crew, who may not have all spoken fluent English, would have received daily food rations worth 13 ¼ cents per inmate and would only be able to take fresh air from inside the jail’s walled courtyards.
The thirteen Dutchmen remained in jail for three weeks, until removed under RCMP guard on the afternoon of Saturday, November 9th; they left Goderich by rail. Their destination upon leaving Huron County was once again a mystery to the media and the public, but widely assumed to be a Canadian internment camp, where POWs, Jewish refugees from Europe, and civilian ‘enemy aliens’ of differing loyalties could be forced to cohabitate.
Captain Helsdingen and the Prins Willem III continued on to Montreal to enter into the service of the allies as originally ordered by the Dutch government-in-exile so many months earlier. The temporary Canadian replacements would eventually be relieved by a Dutch crew, and the boat outfitted with anti-aircraft guns and machine guns, but the Captain was to face continued refusals of work from his crew throughout the war. Confirming the original crew’s fears, an aerial torpedo struck the Prins Willem III off the coast of Algiers in March, 1943; the ship later capsized and sank, resulting in eleven deaths. None of the original crew from the Chicago sojourn were amongst the lives lost.
The international incident caused by the Prins Willem III in the Great Lakes may be largely forgotten today, but the plight of its crew demonstrates that the North American homefront was not always as peaceful or untouched by the conflict in Europe as we might imagine. Overnight, the capitulation of the Netherlands had left the crew of the Prins Willem III in a precarious situation after enduring a surely traumatizing ordeal during the Nazi invasion on May 10th, 1940. Facing uncertainty in the custody of North American authorities, versus what they might have deemed as an almost certain death re-entering a war zone without adequate protections, they took action (or rather inaction) that stymied multiple governments and brought the repercussions of the Second World War to an ‘Ontario Port’ as apparently nondescript as ours.
*A note on spelling: Jail & gaol are alternative spellings of the same word, pronounced identically. Both spellings were used throughout the history of the Huron Historic Gaol fairly interchangeably. Although as a historic site the Huron Historic Gaol uses the ‘G’ spelling more common to the nineteenth century, for this article I have chosen to employ the ‘J’ spelling that appeared more consistently in the 1940s.
** Newspaper reports record 16 crew members jailed, but the Jailer’s Report to Council for 1940 recorded 13 “alien seamen,” and this is also the number given by Martine van der Wielen-de Goede, who reviewed crewmembers’ testimonies later in London (see sources below).
Special thanks to Alana Toulin & Christina Williamson for research assistance that made this blog post possible!
Further Reading
Internment in Canada via the Canadian Encyclopedia: https://thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/internment
Internment resources from Library and Archives Canada: https://www.bac-lac.gc.ca/eng/discover/politics-government/Pages/thematic-guides-internment-camps.aspx
Secondary Sources
Gillham, Skip, “The Oranje Line,” Telescope, Volume XXX, No. 5. (Sept-Oct 1981), pg 116-117.
Malcolm, Ian M, Shipping Losses of the Second World War, (Brinscombe Port Stroud: The History Press, 2013).
van der Wielen-de Goede, Martine, “Varen of brommen Vier maanden verzet tegen de vaarplicht op de Prins Willem III, zomer 1940,” Tijdschrift voor Zeegeschiedenis, No. 1 (Jan. 2008) Via https://docplayer.nl/173449011-Ten-geleide-tijdschrift-voor-zeegeschiedenis.html
Sources: Articles
“At Sea: Open Lanes.” Time Magazine, October 21, 1940, pg 29.
“Canada Jails 16 Dutch Seamen After Mutiny.” Chicago Daily Tribune, October 11, 1940.
“Dutch Crew Jailed.” The Wingham Advance-Times, October 17, 1940.
“Dutch Sailors Removed.” Huron Expositor, November 15, 1940.
“Dutch Sailors to Jail.” Clinton News-Record, October 24, 1940.
“Dutch Freighter Arrives in Goderich.” Clinton News-Record, October 17, 1940.
“Escapes Bombing; Reaches Chicago: Unloads Seeds, Twine.” Chicago Daily Tribune, June 27, 1940.
“Explains Dutch Sailors’ ‘strike’: They Fear Nazis.” Chicago Daily Tribune, July 28, 1940.
“Members of Crew Interned.” The Seaforth News, October 17, 1940.
“Sitdown Strike Strands Dutch Ship in Chicago.” Chicago Daily Tribune, July 26, 1940.
“Stranded Dutch Ship Sails with Canadian Crew: Idle Force Lets Sailors Aboard Quietly.” Chicago Daily Tribune, October 8, 1940.
“Strikers Mark Time.” Chicago Daily Tribune, July 27, 1940.
Wilson, Edward. “Aye, There’s Rub to Life Aboard Dutch Freighter: Crew Keeps Busy Polishing and Painting Ship.” Chicago Daily Tribune, September 7, 1940.

by Sinead Cox | May 7, 2020 | Huron Historic Gaol, Investigating Huron County History
In this two-part series, Curator of Engagement & Dialogue Sinead Cox illuminates how the Second World War impacted Huron County in unexpected ways at home, and even entered the walls of the Huron Historic Gaol. Click for Part Two, and the strange tale of how Dutch sailors became wartime prisoners in Huron’s jail.
During the Second World War, Canada revived the War Measures Act: a statute from the First World War that granted the federal government extended authority, including controlling and eliminating perceived homegrown threats. The Defence of Canada Regulations implemented on September 3, 1939 increased censorship; banned particular cultural, political and religious groups outright; gave extended detainment powers to the Ministry of Justice and limited free expression. In Huron County, far from any overseas battlefields, these changes to law and order would bring the Second World War closer to home.
 Regulations required Italian and German-born Canadians naturalized as citizens after 1929 (expanded to 1922 the following year) to formally register as ‘enemy aliens’ and report once a month. In Huron County, jail Governor James B. Reynolds accepted the appointment of ‘Registrar of Enemy Aliens’ in the autumn of 1939, and the registration office was to operate from the jail in Goderich. There were also offices in Wingham, Seaforth and Exeter managed by the local chief constables of the police force.
Regulations required Italian and German-born Canadians naturalized as citizens after 1929 (expanded to 1922 the following year) to formally register as ‘enemy aliens’ and report once a month. In Huron County, jail Governor James B. Reynolds accepted the appointment of ‘Registrar of Enemy Aliens’ in the autumn of 1939, and the registration office was to operate from the jail in Goderich. There were also offices in Wingham, Seaforth and Exeter managed by the local chief constables of the police force.
In addition to its novel function as the alien registration office, the Huron Jail also housed any prisoners charged criminally under the temporary wartime laws. Inmate records from the time period of the Second World War cannot be accessed, but Reynolds’ annual reports submitted to Huron County Council indicate that one local prisoner was committed to jail under the ‘Defence of Canada Act’ in 1939, and there were an additional four such inmates in 1940. The most common charges landing inmates behind bars during those years were still typical for the county: thefts, traffic violations, vagrancy and violations of the Liquor Control Act (Huron County being a ‘dry’ county).
Frank Edward Eickemier, the lone individual jailed under the War Measures Act’s Defence of Canada regulations in 1939, was no ‘alien,’ but the Canadian-born son of a farm family in neighbouring Perth County. Nineteen-year-old Eickemier pled guilty to ‘seditious utterances’ spoken during the Seaforth Fall Fair, and received a fine of $200 and thirty days in jail (plus an additional six months if he defaulted on the fine). The same month the Defence of Canada regulations took effect, Eickemier had publicly proclaimed that Adolph Hitler’s Nazi Germany was undefeatable, and that if it were possible to travel to Europe he would join the German military. He fled the scene when constables arrived, but was soon pursued and arrested for “statements likely to cause disaffection to His Majesty [King George VI] or interfere with the success of His Majesty’s forces.” His crime was not necessarily his political views, but his disloyalty. The prosecuting Crown Attorney conceded, “A man in this country is entitled to his own opinion, but when a country is at war you can’t go around making statements like that.”
Bruce County law enforcement prosecuted a similar case in July of 1940 against Martin Duckhorn, a Mildmay-area farm worker employed in Howick Township, and alleged Nazi sympathizer. Duckhorn had been born in Germany, and as an ‘enemy alien’ his rights were essentially suspended under the War Measures Act, and he thus received an even harsher punishment than Eickemier: to be “detained in an Ontario internment camp for the duration of the war.”

Huron County Courthouse & Courthouse Square, Goderich c1941. A991.0051.005
In July of 1940, the Canadian wartime restrictions extended to making membership in the Jehovah’s Witnesses illegal. The inmates recorded as jailed under the ‘Defence of Canada Act’ in Huron that year were likely all observers of that faith, which holds a refusal to bear arms as one its tenets, as well as discouraging patriotic behaviours. That summer, two Jehovah’s Witnesses arrested at Bluevale and brought to jail at Goderich ultimately received fines of $10 or 13 days in jail for having church publications in their possession. Four others accused of visiting Goderich Township homes to discourage the occupants from taking “any side in the war” had their charges dismissed—due to a lack of witnesses. In 1943, the RCMP and provincial police collaborated to arrest another three Jehovah’s Witnesses in Goderich Township for refusing to submit to medical examinations or report their current addresses (therefore avoiding possible conscription); the courts sentenced the three charged to twenty-one days in the jail, afterwards to be escorted by police to “the nearest mobilization centre.”
By August of 1940, an item in the Exeter Times-Advocate claimed that RCMP officers were present in the area to ‘look up’ those individuals who had failed to comply with the law and promptly register as enemy aliens. A few weeks later, the first Huron County resident fined for his failure to register appeared in Police Court. The ‘enemy alien’ was Charles Keller, a 72-year-old Hay Township farmer who had lived in Canada for 58 years, emigrating from Germany as a teenager in 1882. According to his 1949 obituary in the Zurich Herald, Keller was the father of nine surviving children, a member of the local Lutheran church, and had retired to Dashwood around 1929. His punishment for neglecting to register was not jail time, but the fine of $10 and costs (about $172.00 today according to the Bank of Canada’s inflation calculator).
Although incidences of prosecution under the ‘Defense of Canada Act’ in Huron County were few, the increased scrutiny and restrictions would have been felt in the wider community, especially for those minority groups and conscientious objectors directly impacted. Huron had a notable number of families with German origins, especially in areas like Hay Township where you can still see the tombstones of many early settlers written in German. The Judge who sentenced Frank Edward Eickemier for his public support of the Nazi regime in 1939 made a point of accusing him of casting a ‘slur’ on his ‘people’ and all German Canadians: the actions of the individual conflated with a much larger and diverse German community by a representative of the law. His case indicates that pro-fascist and pro-Nazi sentiment certainly did exist close to home, but a person’s place of birth or their religion was not the crucial evidence that could define who was or was not an ‘enemy.’
Next Week: Click for Part Two, and the strange tale of how stranded Dutch sailors ended up prisoners in the Huron County Jail during the Second World War.
*A note on spelling: Jail & gaol are alternative spellings of the same word, pronounced identically. Both spellings were used throughout the history of the Huron Historic Gaol fairly interchangeably. Although as a historic site the Huron Historic Gaol uses the ‘G’ spelling more common to the nineteenth century, for this article I have chosen to employ the ‘J’ spelling that appeared more consistently in the 1940s.
Further Reading
The War Measures Act via the Canadian Encyclopedia
Sources
Research for this blog post was conducted largely via Huron’s digitized historical newspapers.
“Faces Trial on Charge of Making Disloyal Remark.” Seaforth News, September 28, 1939.
“German Sympathizer Interned.” The Wingham-Advance Times, July 25, 1940.
“In Police Court.” Seaforth News, August 29, 1940.
“Jehovah’s Witnesses Charged.” Zurich Herald, October 21, 1943.
“Jehovah’s Witnesses Fined at Goderich.” The Wingham-Advance Times, August 22, 1940.
“Jehovah’s Witnesses Refused Bail.” The Wingham Advance-Times, July 18, 1940.
“Looking Up Aliens Who Failed to Register.” The Exeter Times-Advocate, August 1, 1940.
“Police Arrest ‘Jehovah’s Witnesses.’” Seaforth News, June 27, 1940.
“Statement He Would Fight for Hitler Proves Costly.” The Wingham-Advance Times, October 5, 1939.
“To Register German Aliens.” The Seaforth News, October 12, 1939.
“Twenty-One Days.” The Lucknow Sentinel, October 28, 1943.
“Would Fight for Hitler-Arrested.” The Wingham Advance-Times, September 28, 1939.





















