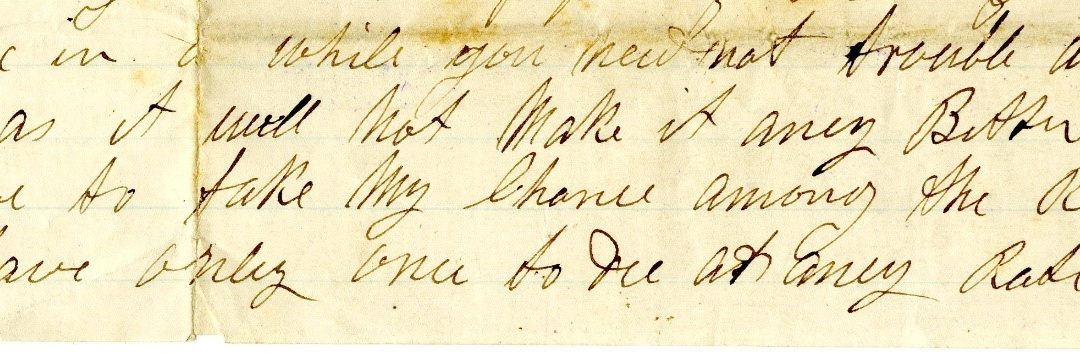
New to the Collection: Civil War Letters
“I shall have to take my chance amongst the rest. I have only once to die at any rate.” – excerpt from a letter written by Joseph Hodskinson, March 29, 1862
The American Civil War doesn’t usually come to mind when thinking about Huron County history, but a recent donation to the Huron County Archives reveals the devastating impact the war had on a Brussels family.
Joseph Hodskinson immigrated to Canada from Scotland around 1851 with his wife Margaret and daughter Celina. The family settled in the Brussels area where Joseph worked as a farmer before he joined the Civil War. It remains unknown why Joseph chose to leave his family in Canada to join the fight in America, but what is known is he would never return home.
The American Civil War was fought between the Union (the North) and the Confederacy (the South – formed by states that had seceded) from April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865. According to Wikipedia, “the central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.”

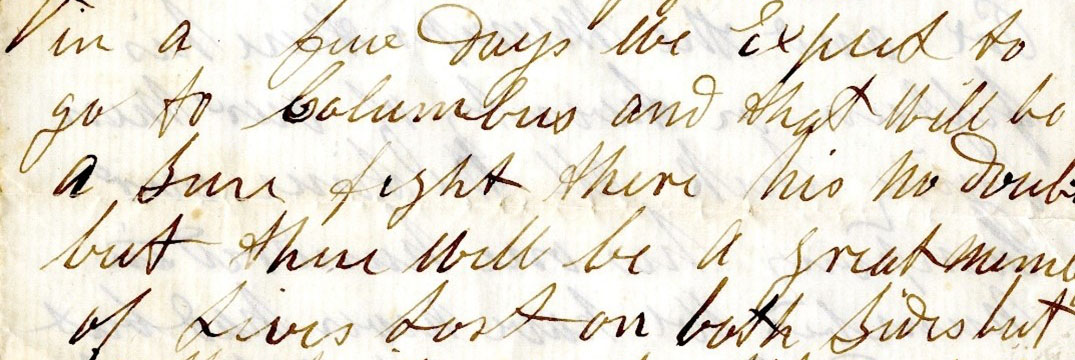
“We expect to go to Columbus and that will be a sure fight. There is no doubt but there will be a great number of lives lost on both sides.” – excerpt of a letter written by Hodskinson on Jan. 24, 1862
Between 1862 and 1863, Joseph wrote several letters home to Margaret and Celina, describing the horrors of war. In the first winter of the war, in January 1862, he shares the great deal of sickness that hit the soldiers, including measles, small pox and mumps. In a letter home on March 1862, he describes three days of fighting at the Battle of Fort Donelson and noted that “It is the providence of the Lord that I am amongst those that was saved on the 13th Feb….the morning after the battle the field was a fearful sight. You might almost walk on dead bodies for a long distance.” A letter home on June 12, 1862, reveals that “We only have about 300 men remaining out of 1000 since I joined the army.”
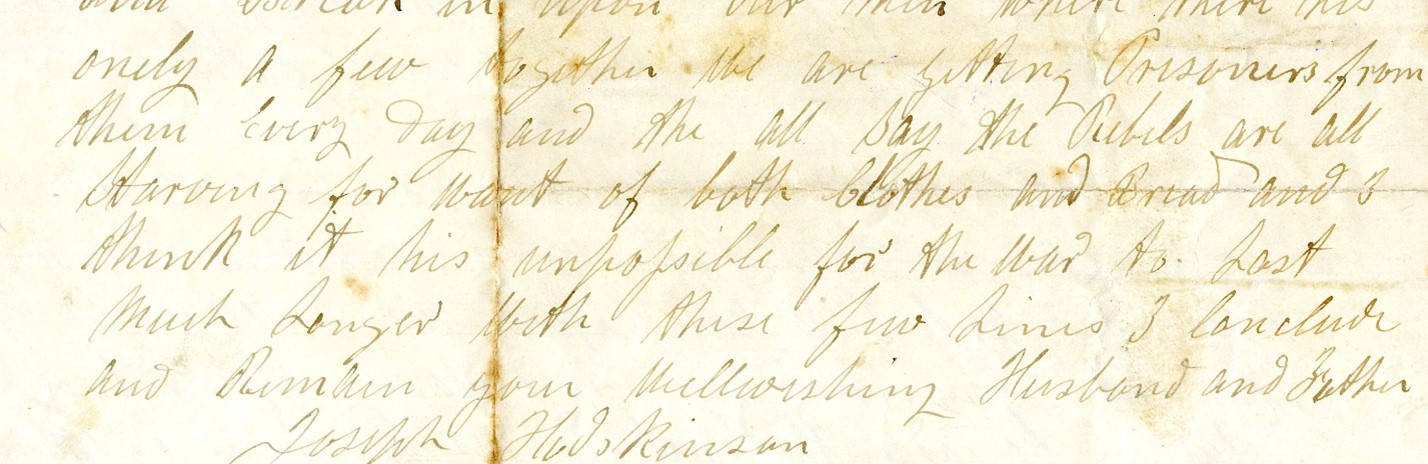
We are getting prisoners from them every day and they all say the Rebels are all starving for want of both clothes and bread and I think it is impossible for the war to last much longer.” – excerpt from a letter dated Jan. 2, 1863
The war would continue for two more years, but Joseph would not see the end of the war, nor would he make his way home to his family in Brussels. He died later that year.
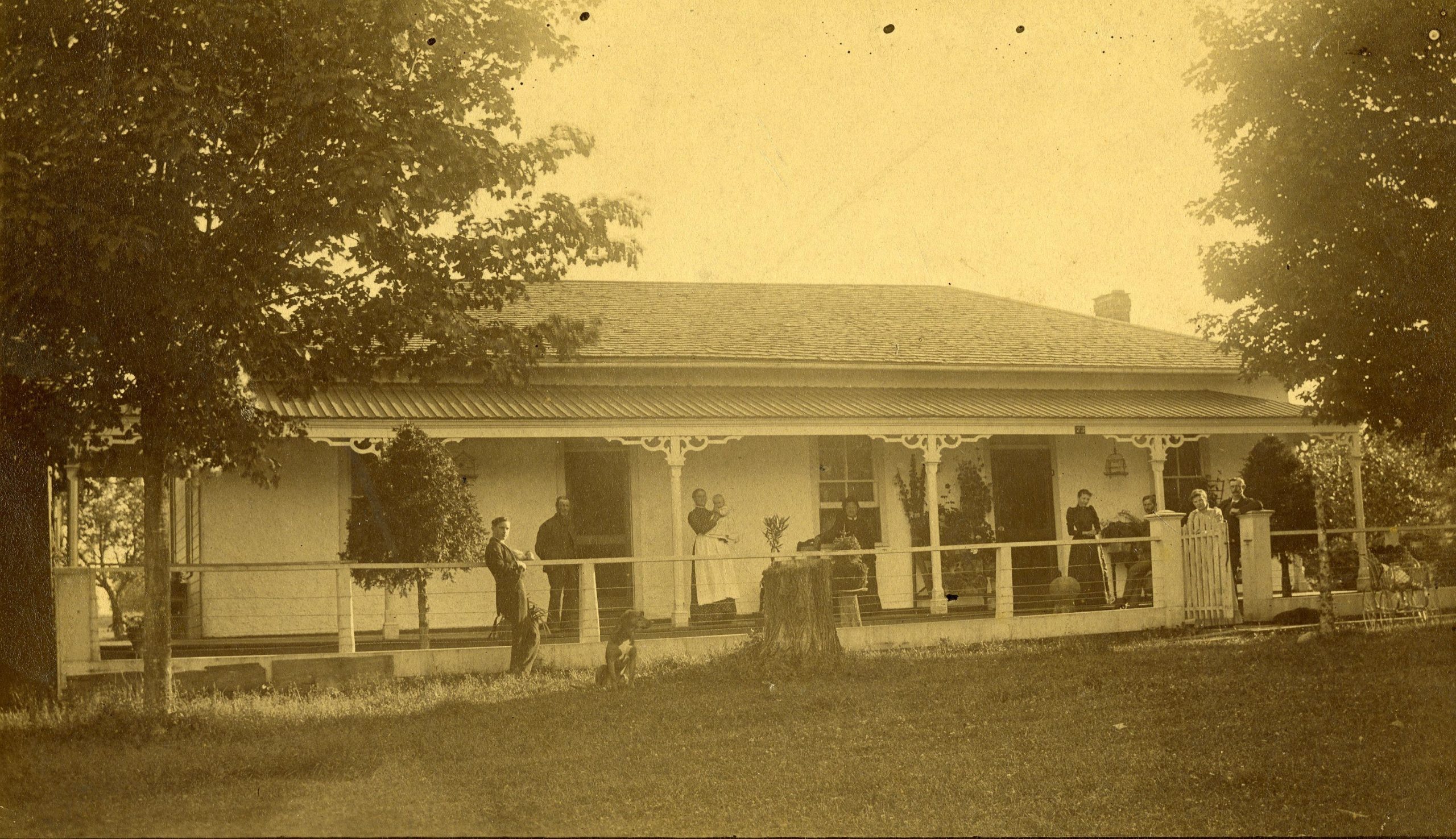

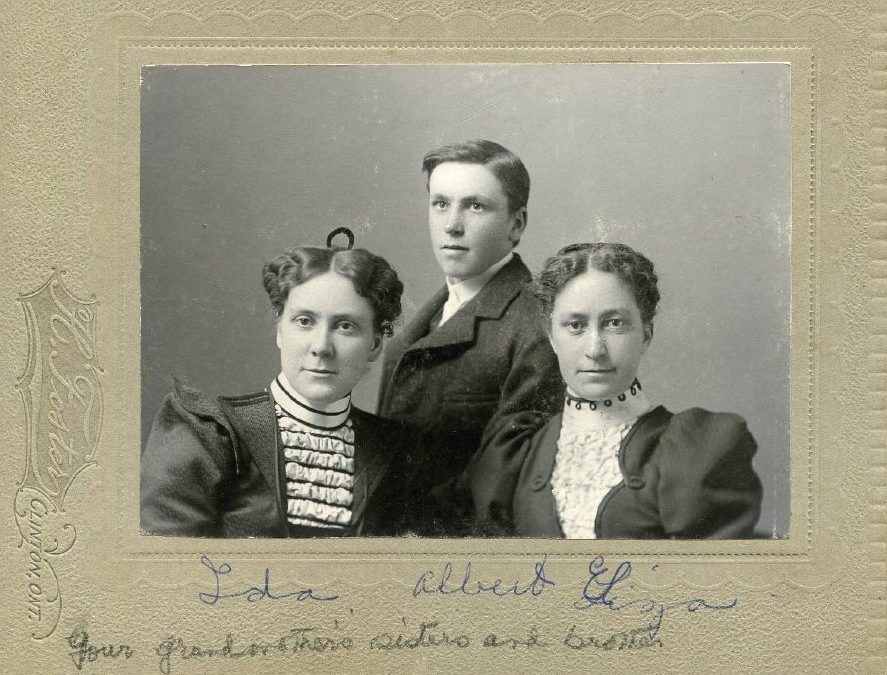
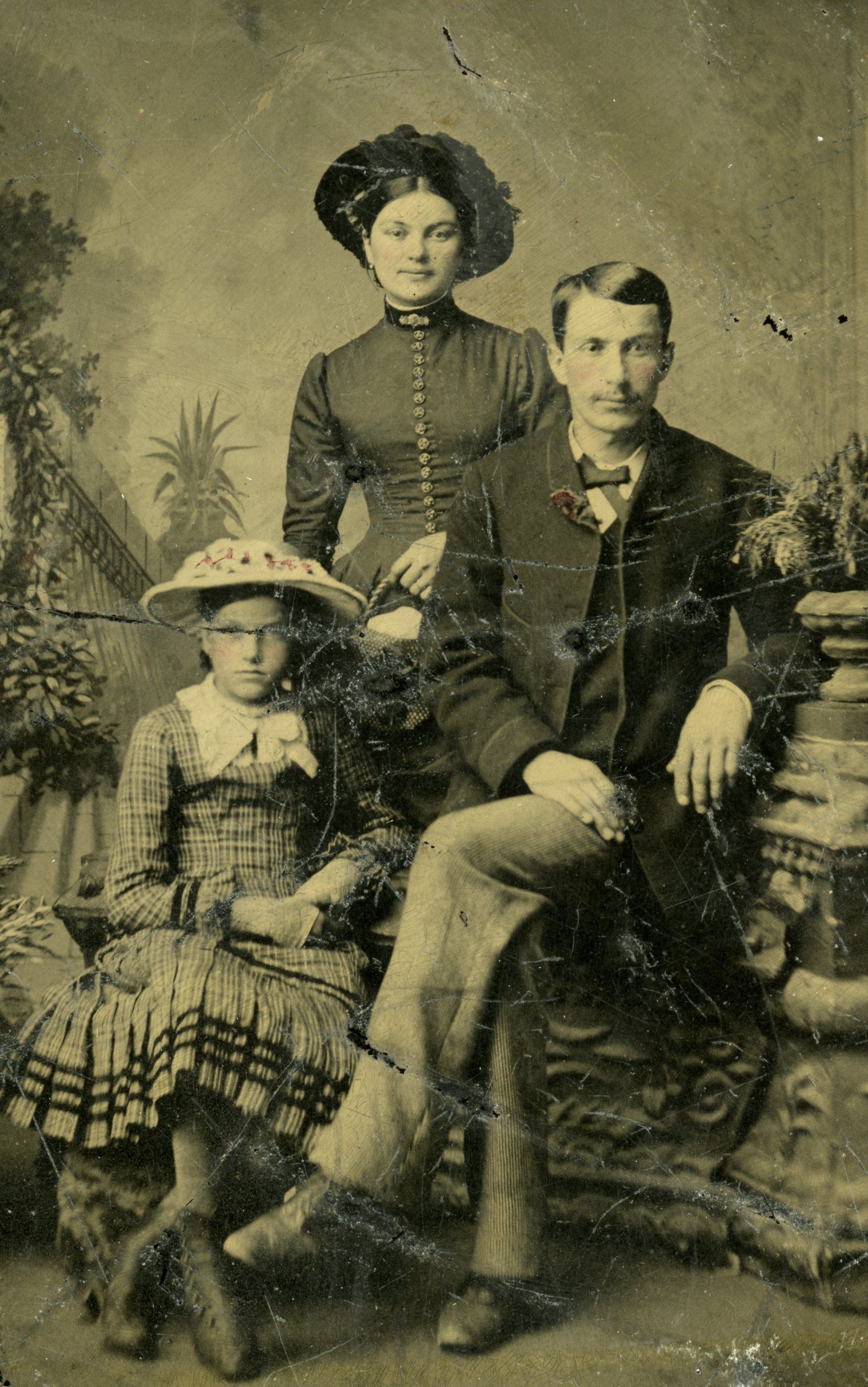
After Joseph’s death, Margaret and Celina remained in the Brussels area. Celina married Thomas Ballantyne in the fall of 1862 and the couple made their home on the bank of the Maitland River in the spring of 1863. The home is pictured above with the family sitting on the front porch around 1892. Shown here, from left to right, are Jack Ballantyne, Thomas Ballantyne, Celina Ballantyne holding Bill Strachan, Margaret Hodskinson, Annie and Alex Strachan, and Jenny and Joe Ballantyne.
Celina and Thomas had a daughter named Annie who married Alexander Strachan in Brussels in 1889. The couple owned a dry goods store in the village.
The Huron County Museum would like to thank Ann Scott and Marion MacVannel for their recent donation of these letters and family photographs to the archival collection. Joseph was Ann’s three times great grandfather. If you are interested in learning more about our research services or making a donation to our collection, contact the Huron County Archives to arrange an appointment.