by Amy Zoethout | Jul 25, 2023 | Blog, Huron Historic Gaol
Written by museum assistant Kevin den Dunnen, who is working on exhibit research projects this summer.
Over 6,600 people came through the Huron County Gaol’s long and narrowing hallway between 1841 and 1922. For each entry into the Gaol, employees recorded information about that person such as the crime they committed, the institution they transferred to, their age, height, eye colour, relationship status, residence, religion, sentence length, etc. This registry is essentially a brief snippet into a person who, in many cases, would otherwise never have such detailed information about their lives presented for historical interpretation. A new exhibit at the Huron Historic Gaol presents an analysis of the people who came to the Gaol through the registry up until 1922. While the Gaol operated until 1972, due to privacy restrictions, staff can only access registry entries after they are 100 years old.
Interpreting more than 6,600 distinct entries in the Gaol Registry presents a challenge to museum staff who must comb through this information to provide accurate data about the prisoners of the Gaol. As part of my programs at school, I interpreted quantitative data and presented visually engaging infographics for public audiences. It was during my employment at the Huron County Museum & Historic Gaol last summer that I recognized the Gaol Registry is compatible with business intelligence software I used in school. This allowed me to present the data as an interactive infographic, giving Museum staff the ability to easily analyze information such as the crimes committed, residence, and religion of prisoners at the Gaol. In this way, staff can answer questions such as the makeup of crime from differing communities in Huron County in a matter of minutes rather than hours.
With so much information available, much of the information in the Gaol Registry did not make it into the new exhibit. For instance, the makeup of prisoner height is difficult to correlate into an overarching exhibit theme. In this blog, however, I can tell you that the most common height for male prisoners was 5’ 8” with 13.6%, while 5’ 6”, 5’ 7”, and 5’ 9” round out the top four and are each above 10% of the male prisoner population. For female prisoners, 5’ 5” was the most common height with 17.7%, while 5’ 2”, 5’ 4”, and 5’ 3” fill out the top four with each above 11% of the female prisoner population.
The crime demographics for places of residence is another interesting data set that did not make it into the exhibit. For Goderich-based prisoners, drunkenness was the most common crime with vagrancy second. Prisoners registered from Wingham most commonly committed larceny with vagrancy second. Prisoners from Seaforth most often came in for vagrancy, followed closely by assault and then drunkenness. Prisoners from Exeter most often committed larceny, followed by assault and then vagrancy.
Since Huron County was one of the last dry counties in Ontario, temperance, or the act of professing abstinence from alcohol, was commonly recorded by gaol staff. Some stories relating to temperance feature in the new exhibit, but it is possible to analyze this information further using business intelligence software. For instance, Clinton prisoners recorded one of the highest percentages of temperance. Almost 48% of prisoners from Clinton were temperate. We can analyze this data another step through gender. 85% of females from Clinton declared temperance. In comparison, Gaol staff recorded 34% of Goderich residents as temperate. 49% of female prisoners from Goderich were temperate. We can further interpret the Clinton dataset using religion. While almost 20% of all prisoners from Clinton were Methodist, 43% of temperate prisoners from Clinton were Methodist.
The last information I will share with you in this post is marital status. 54% of prisoners who came through the Gaol’s long, narrowing hallway, were single, 40% of prisoners were married, and 6% were widowed. This information remains consistent within a few percentage points across residences like Goderich, Exeter, Lucknow, Seaforth, Wingham, and Clinton.
These are but a few facts outlined in the registry and staff continue to use these details as they research prisoners and their lives at the Gaol.
Want to learn more about the lives of prisoners from the Huron County Gaol? Come visit the new exhibit and speak with our staff about the Gaol Registry.
From the Huron Historic Newspaper collection. Published in The Signal, 1913-11-6, Page 6
The owners of this whisky jug came by boat to Goderich then walked through the Queens Bush to homestead near Teeswater and Langside. The jug was carried slung over a stick on the back of a man when he walked through the Queens bush to barn and house raisings. The MacDougall’s often went to raisings 50 miles away (Goderich) after clearing bush near Langside, Bruce County. Object ID: M9590109001

by Sinead Cox | Dec 29, 2022 | Huron Historic Gaol, Investigating Huron County History
“No Possible Escape” sounds positive when it comes to jailbreaks, but less so in the case of emergency. Curator of Engagement & Dialogue Sinead Cox looks back at fire and fire safety at the Huron Historic Gaol.
The Huron Historic Gaol is one of the most recognizable, historically significant and architecturally unique buildings in Huron County. Today it stands as a venue for visitors to hear the stories of the prisoners and staff who walked its halls, and considering the number of times the building has caught fire over its 180+ year history, this is nothing less than a small miracle.
Although the outer walls may give the impression that it is solid stone, the construction of the gaol interior is actually significantly timber. The unique octagonal layout of rooms and yards around a central spiral staircase are designed to keep prisoners in, with perhaps less architectural forethought when it comes to allowing people to quickly get out, should the upper floors become engulfed in flames.
In 1851, when the building was only a decade old and served the United Counties of Huron, Perth and Bruce, an errant chimney spark caused the first known fire of significance. Fortunately, the only harm sustained in that instance was damage to the building’s roof. Afterwards, the Gaol Inspector recommended covering the roof with metal, and that the county purchase a new ladder tall enough to actually enable water to be carried high enough to fight a fire (staff presumably having discovered the inadequacies of the previous ladder during the emergency). No ladder would have been very useful as a means of rescue for prisoners, however, as all of the windows on the gaol’s upper floors were barred to prevent escape.
In the 1860s the County of Huron replaced the tin-covered roof with slate, later swapped for asphalt shingles about a century later. When reverting to slate in 2021, roofers discovered lumber inside the cupola still bore blackened scorch marks from historic fires. The cupola, or central tower, has been struck by lightning at least twice: in 1892 and 1929. Torrential rain prevented fire in the first case, but the second strike “set the tower ablaze” just after one a.m. According to The Clinton News Record, “a terrific electric storm was in progress and firemen had difficulty at first in plying streams of water on the tower, owing to its height. Some of the firemen climbed on to the slate roof, slippery with rain, and fought the flames from perilous positions.” The newspaper claimed that despite the late hour and extreme weather, a crowd of people gathered outside the gaol’s walls to watch their efforts. While firefighters risked their lives to stop the fire from spreading to the lower floors, a constable escorted the seven prisoners currently committed to the Huron Gaol to an outside courtyard, still confined within the 18 ft walls. Thankfully, the fire was successfully contained within the cupola and extinguished, but the flames and the water employed to douse them had caused more than $1,000 in damages (equal to just over $16,500 today). The county enlisted prisoner labour to help with the subsequent clean-up and repairs.

Fire bucket. M951.0732.001
Huron Historic Gaol, Goderich Ontario
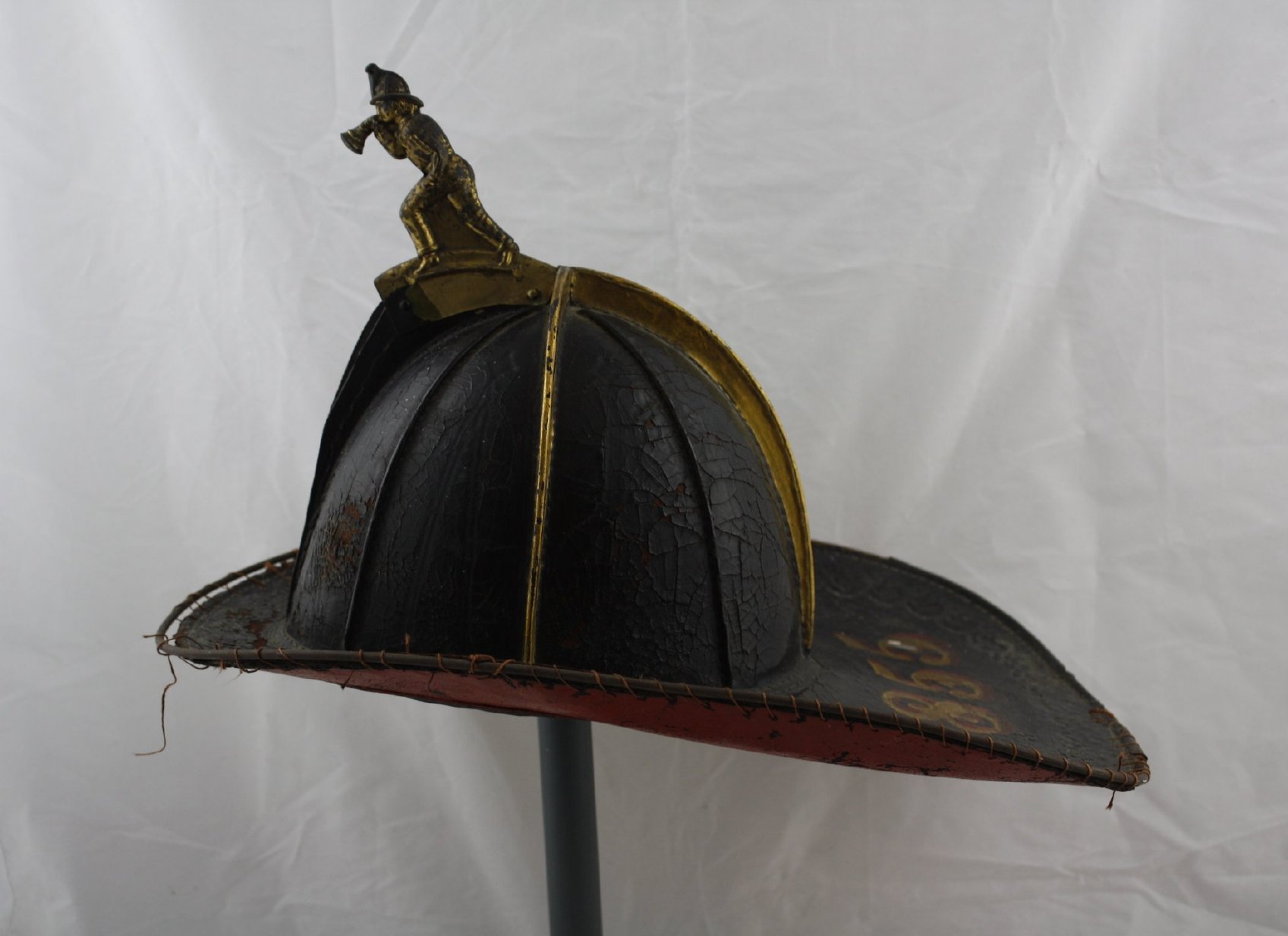
1855 Fireman’s helmet donated by Town of Goderich. M951.0734.001.
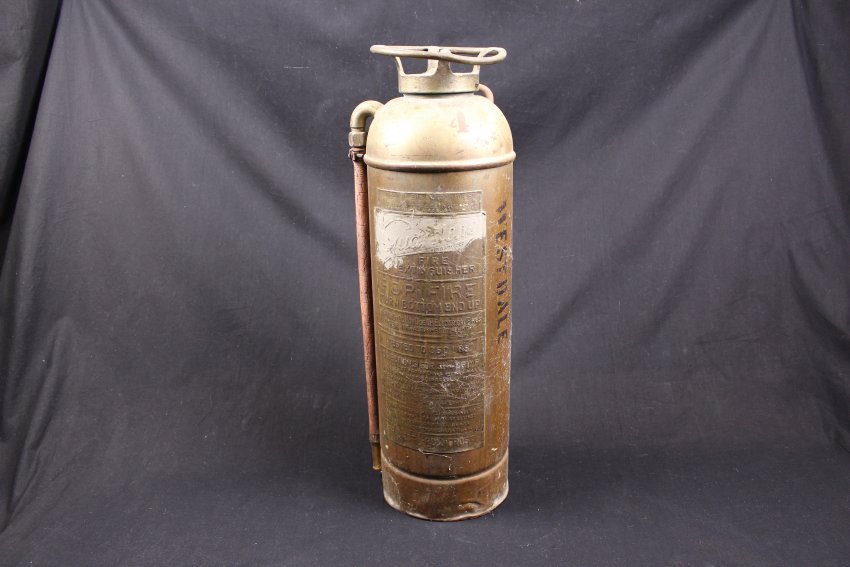
Fire Extinguisher. 2017.0024.003.
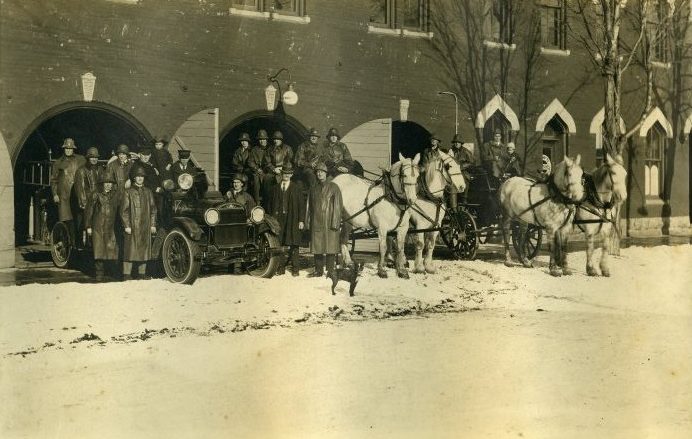
A950.1976.001. Fire crew at former Goderich Fire Station located on East Street, 1925.
The cupola caught fire again in 1944, this time from burning leaves, either carried from the ground by a strong wind or ignited in the eaves by a spark. Although this fire burned only briefly, it caused destruction and water damage similar or worse than the 1929 blaze: costs duly submitted to the county’s insurer.
Officials and staff recognized the inadequacies of the gaol’s design very early in its operation: the lack of fire exits was one of the reasons that District Council and the courts complained about meeting there before the construction of a separate courthouse in 1856. Despite the general awareness of the threat, safety measures provided by the county did not always meet the needs of staff or emergency responders. After the 1892 lightning strike, Gaoler William Dickson found that the gaol’s fire hose was faulty, and burst in multiple places when tested with pressure. As early as 1882, after yet another recent narrow escape from flames, local newspaper editorials from the Goderich Star and Clinton New Era condemned the gaol as an outdated fire trap. The Era argued for replacing the gaol and courthouse with new, modern municipal buildings in a more central location. The Gaol and Court House Committee instead recommended “that a Babcock Fire Extinguisher for the gaol be furnished, also that a suitable water tank be built in the gaol yard, owing to the inflammable and unsafe condition of the gaol stairs, there is no possible escape for the inmates in case of fire.”
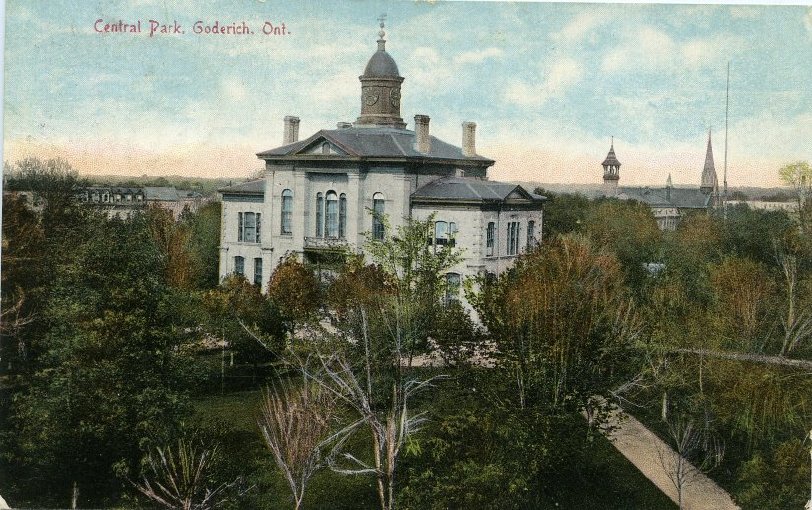

Postcard of courthouse at “Central Park” or Square, Goderich. Built 1856. This courthouse was destroyed by fire and replaced in 1954. 2008.0032.083.
In the 1890s, Huron County Council acknowledged the aging heating stoves in each cell block’s dayroom as another serious danger and replaced them. Prior to electric lights, staff also had to contend with mandatory corridor lamps, burning day and night at the risk of overheating. Gaoler Dickson lamented to County Council in 1896 that, “twice [a lamp has exploded] during the almost 32 years I have been in your employ. The last time it was towards morning and fortunately my subordinate was awake and succeeded in extinguishing the fire at the cost of the bedding of two beds.” Dickson credited the turnkey’s quick action in preventing what was nearly a terrible tragedy: “At the time of the explosion there were 18 prisoners under lock and key, besides 5 members of my own family who were sleeping on the second floor. Had the flames caught the stair, all on the upper floors would have been entirely cut off from escape. In view of this danger to life and property, I would respectfully ask that you place one incandescent in said hallway.” The gaoler’s lobbying successfully resulted in the installation of incandescent lights at the gaol, but the issue of the single exit remained unaddressed. It’s easy to imagine that if the fire had spread beyond the smothering power of gaol blankets, that a quick decision may have been made to prioritize the evacuation staff and family before the overcrowded inmates sleeping behind multiple locked doors.
The close-call fires at the gaol over the decades were all seemingly accidental, with the exception of one incident during the holiday season in 1943. The gaol’s annual Christmas celebrations included a special meal for the prisoners with treats donated by the community, and that year they also enjoyed a decorated Christmas tree. On December 27th, the dry boughs of the tree caught fire in one of the cell blocks, spreading to the woodwork and choking that ward with thick smoke. The Goderich fire department responded to gaol staff’s call for help, and successfully extinguished the flames in a manner of minutes. A follow-up investigation found that the cell block’s three resident inmates had intentionally started the fire to create a distraction for escape. Convicted forger Floyd McCullough admitted to helping his teenaged cellmates, Angus Trudeau and Lorne Derevere, in devising how to ignite the Christmas tree remnants. The two younger men, committed for robbing Bayfield-area cottages, ultimately also pled guilty to the arson. No opportunity for jailbreak had ever actually materialized as planned; the trio were simply evacuated to another part of the gaol to avoid the smoke inhalation that may have endangered their lives if not for a turnkey’s quick arrival on the scene. All three faced added time behind bars for the conspiracy.

The aging building’s vulnerability to fire remained a concern throughout the twentieth century, resulting in a fire-proof coating applied to the cells in 1939, various furnace installations and upgrades, and an alarm system installed by the 1950s. Jurisdiction over Ontario’s county correctional facilities transferred to the Province in 1964, and in 1972 the Ontario Department of Correctional Services decided to close the Huron Gaol. From 1974, the gaol opened its doors as a historic site and museum, originally managed by the Historic Jail Board– the County of Huron retained responsibility for fire insurance. The County resumed direct control of the building in the 1990s.
The Huron Historic Gaol would pass its 175th birthday before finally gaining a fire escape and new fire exits on the second and third floors of the gaol after major upgrades in 2018. The work was undertaken with care to protect the site’s historical appearance and architecture. As a historic site, fire safety could be addressed to meet contemporary standards without concerns about compromising security. Today, the spectre of potential disaster by fire need not haunt staff and visitors to the degree it once did generations of prisoners and gaol employees. The gaol’s countless near misses with destruction are a reminder of the importance of adequate preparations and equipment to combat fire, as well as the need for strict safety regulations for public buildings. It is only a mixture of ad hoc precautions, the quick actions of the gaol’s small staff, the intervention of local firefighters and also simple luck, that has successfully preserved this one-of-a-kind building and the lives of those who have lived and worked within its walls over three separate centuries.
Find out More!
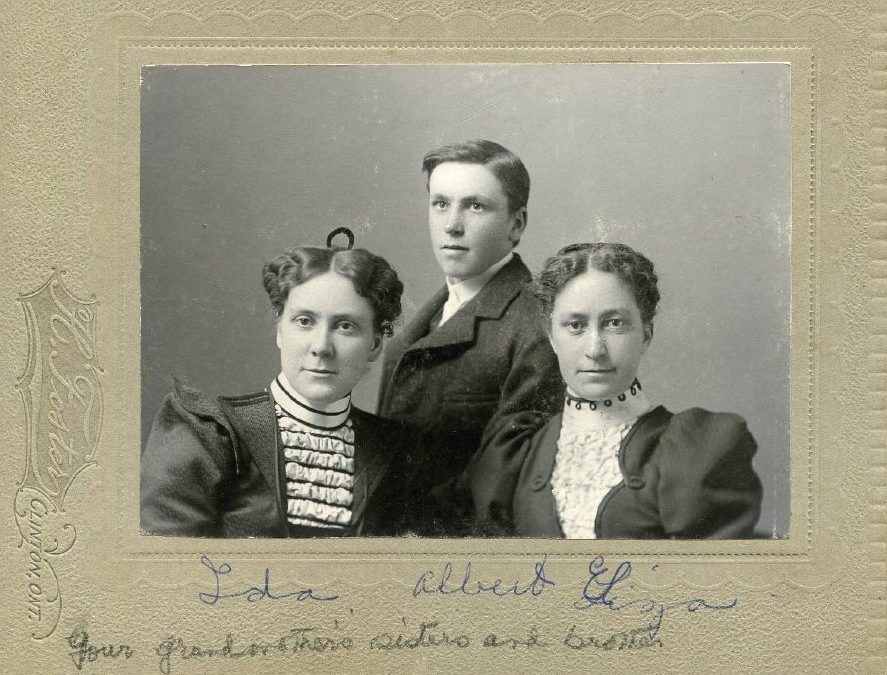

by Sinead Cox | Jan 25, 2022 | Archives, Exhibits, Image highlights
The Huron County Museum’s temporary exhibit Forgotten: People and Portraits of the County features unidentified portraits captured by Huron County photographers. In addition to the onsite exhibit, photos are shared in an online exhibit and Facebook group in hopes that some of these ‘Forgotten’ faces will remembered and named. Curator of Engagement & Dialogue Sinead Cox shares highlights of the exhibit’s remembering efforts so far.

Semi-Weekly Signal, (Goderich) 07-27-1869 pg 2
The Huron County Museum has an incredible collection of photographs in its Archives – especially studio portraits from commercial photographers within Huron County (spanning the county from Senior Studio in Exeter, Zurbrigg in Wingham, and everywhere in between). Not all of these photographs came with identifying information for their subjects, or even known donors or photographers. The Forgotten exhibit has provided an opportunity to delve deeper into the clues that can be present in everything from associated family trees to fashion styles, photographer’s marks, and photography methods that can provide more context, narrow timelines, or even lead to the re-discovery of names. I am especially grateful for the enthusiastic participation we have already had from photo detectives from the public who have contributed to remembering Huron County’s ‘Forgotten’ faces. Hopefully this is just the beginning of adding value to our collection.
Professional studio photographs were often (and still are!) sent as gifts to family and friends. Local photographers saved negatives to sell reprints at a later date, and these negatives were also sometimes inherited when a studio changed hands. It’s very possible your own family photo collection contains the duplicate of a photo that exists in the possession of an archive or a distant relation somewhere else in the world. Finding matches between the faces in those photos is one way to solve photographic mysteries, and why a shared space to upload and comment on photos, like the Forgotten Facebook group, has the potential to put names to faces even after more than a century has passed since the camera flash!
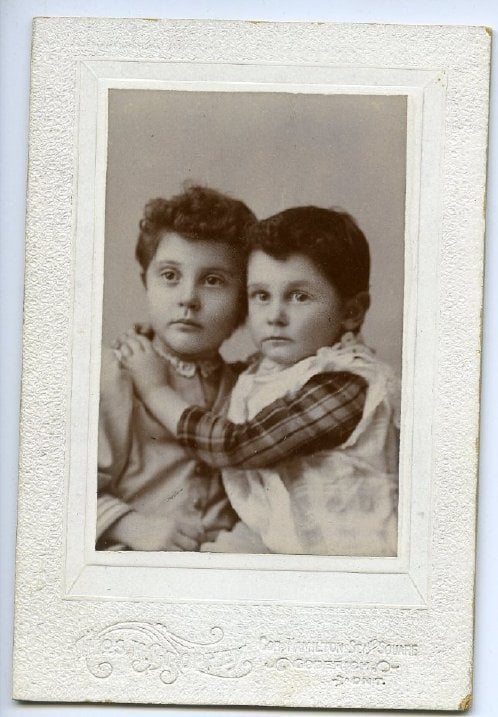

2011.0013.020. Photograph

2017.0013.011. Glass negative
During preparation for the exhibit, staff recognized that a photograph and a glass negative from unrelated donations depicted the same image of a pair of children (their nervous expressions at having their photo taken were difficult to miss). The photo and negative came to the museum from different donors, six years apart. Information provided with the donation of the photograph indicates that these children may be related to the McCarthy and Hussey families of Ashfield Twp and Goderich area; the studio mark for Thos. H. Brophey is also visible on its cardboard mount, dating the image approximately between 1896 and 1904. The matching negative came from a collection related to Edward Norman Lewis, barrister, judge and MP from Goderich. The shared connection between the donations provides one more clue to help identify the unnamed children, and gives the negative meaning and value (through a place, time and potential family connection) it didn’t previously have without the photograph’s added context. You can see both the photograph and the negative on display in the temporary Forgotten exhibit, which is on at the Museum until fall 2022.
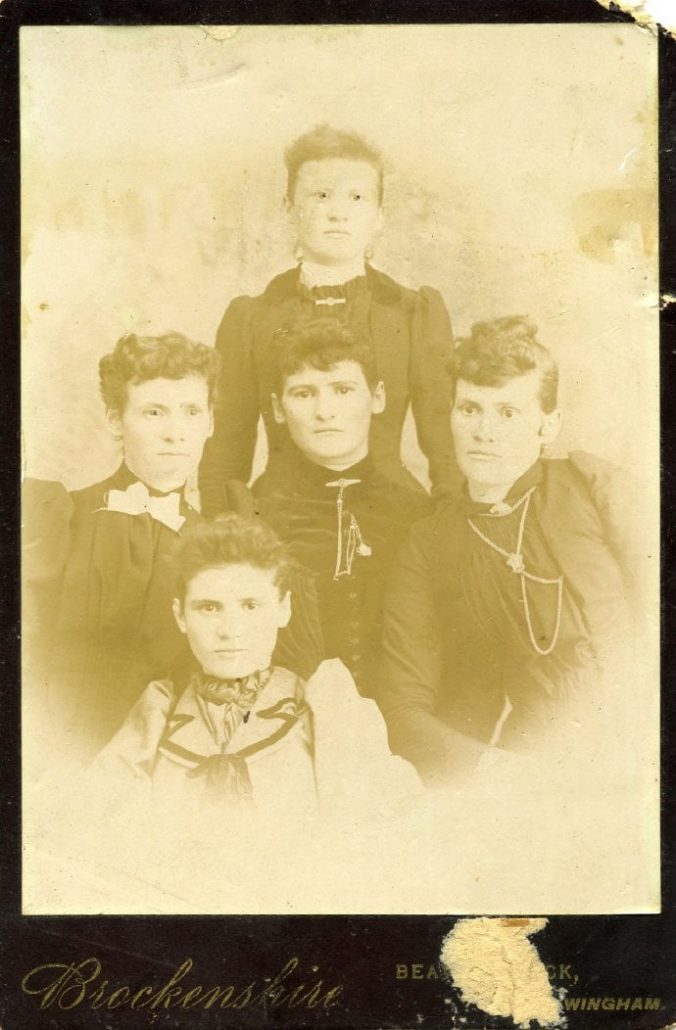

2021.0053.006. The “Garniss sisters”: Sarah Ann, Elizabeth, Eliza Maria Ida, Jemima, Mary Lillian. Can you help us identify which sister is which?
Sometimes photographs arrive to the collection with partial identifications or known connections to a certain family, even when individual names are missing. In those cases, knowledge of family histories can help pinpoint who’s who. Members of the Facebook group were recently able to name all five Morris Township women identified as only the “Garniss sisters” on the back of a photo from Brockenshire Studio, Wingham.
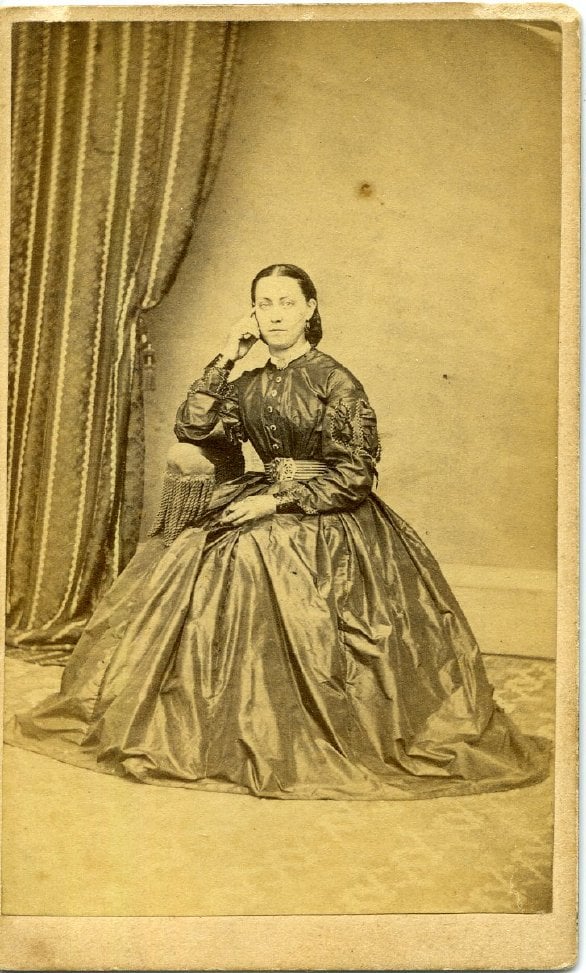

A996.001.095
Patterns tend to emerge with access to larger collections from the same location or time period. Although studio photographers later in the 19th century prided themselves on offering a large selection of backdrops, photos from local studios in the 1860s and 1870s often show a more simple set-up. In posting the ‘Forgotten’ photos online, I noticed that the studio space of Goderich photographer D. Campbell can be recognized by the consistent presence of a striped curtain in the background (and more often than not the same tassel-adorned chair) and a distinctive pattern on the floor, as seen in both the photos above and below. This helped identify additional photographs as Campbell’s work, and therefore place them in Goderich circa 1866-1870 , even when a photographer’s mark or name was absent from they physical photo.
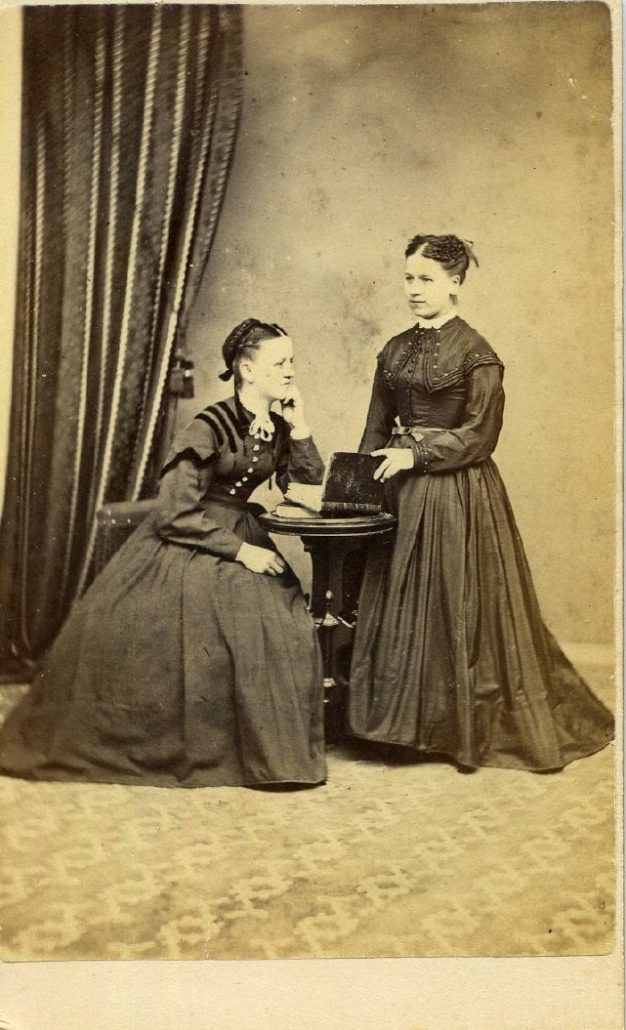

A996.001.071. This photograph is labelled as “the Miss Henrys.” Do you have any information that might reveal their first names?
Crowdsourcing information through the online exhibit and group has allowed fresh pairs of eyes to notice detail previously missed in some of the museum’s photos, even when the evidence was captured by the staff doing the scanning and cataloguing work. In November, the Facebook group spotlighted unidentified soldiers, and one of the members pointed out a photographer’s mark embossed on the bottom right corner of a group photo. Staff were able to look at the original photo to get a clearer look to confirm the studio was identified as “G. West & Sons, Godalming.” Godalming is a town in Surrey, England near Witley Commons, which hosted many Canadian soldiers during the First and Second World Wars.
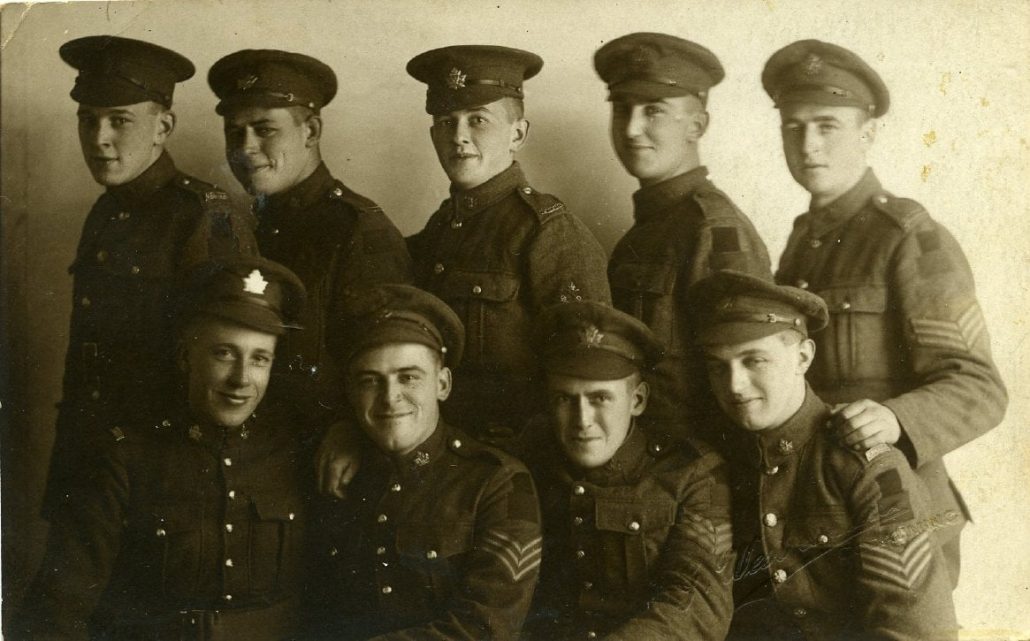

2004.0044.005. Photographer: G. West & Sons, Godalming, Surrey, U.K.
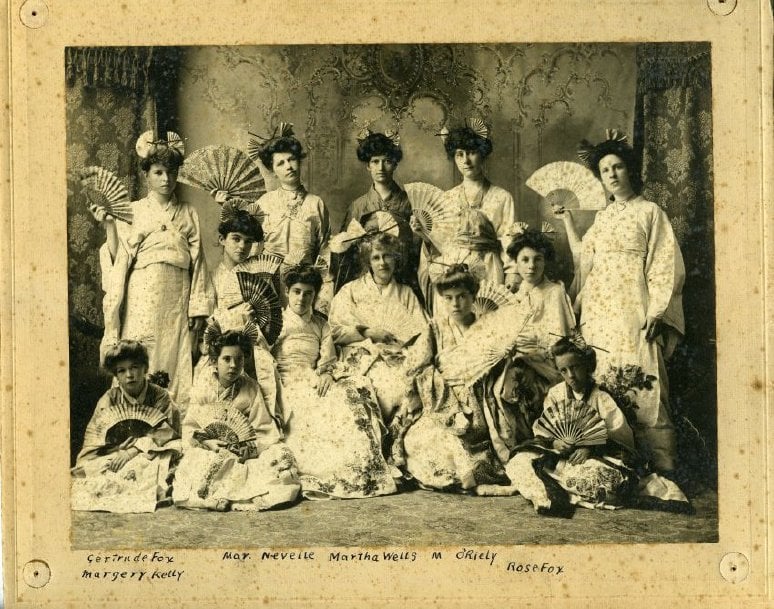

A950.1740.001
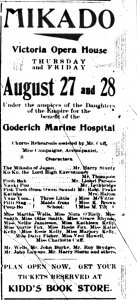
The Signal 08-27-1903 pg 8.
Comparing photographs with other readily available local historical resources like Huron’s digitized newspapers can also help provide new insight. Partial identifications on a group photo of young women in theatrical costumes without a location allowed a group member to link it to a 1903 Goderich production of Gilbert & Sullivan’s The Mikado. Further research in the newspapers provided a full list of the names of the participating cast and more information about the production, which toured Huron County. This information is now attached to the photograph’s catalogue record to benefit future researchers.
Although many historical photos may be ‘Forgotten’, if they are preserved and housed they are not lost. They still retain the potential for remembering , and to be re-connected to descendants and communities through extant clues and the growing possibilities of digitization and online sharing. For more highlights from the exhibit and tips for identifying mystery subjects photos or caring for your own collections, join is Feb. 9, 2022 for the second webinar in our exhibit series: Forgotten in the Archives.
If you can help identify a ‘Forgotten’ face, email us at museum@huroncounty.ca!
For more on the Forgotten: People & Portraits of the County exhibit and related coming events:

by Amy Zoethout | Mar 11, 2021 | Collection highlights, Textile Collection
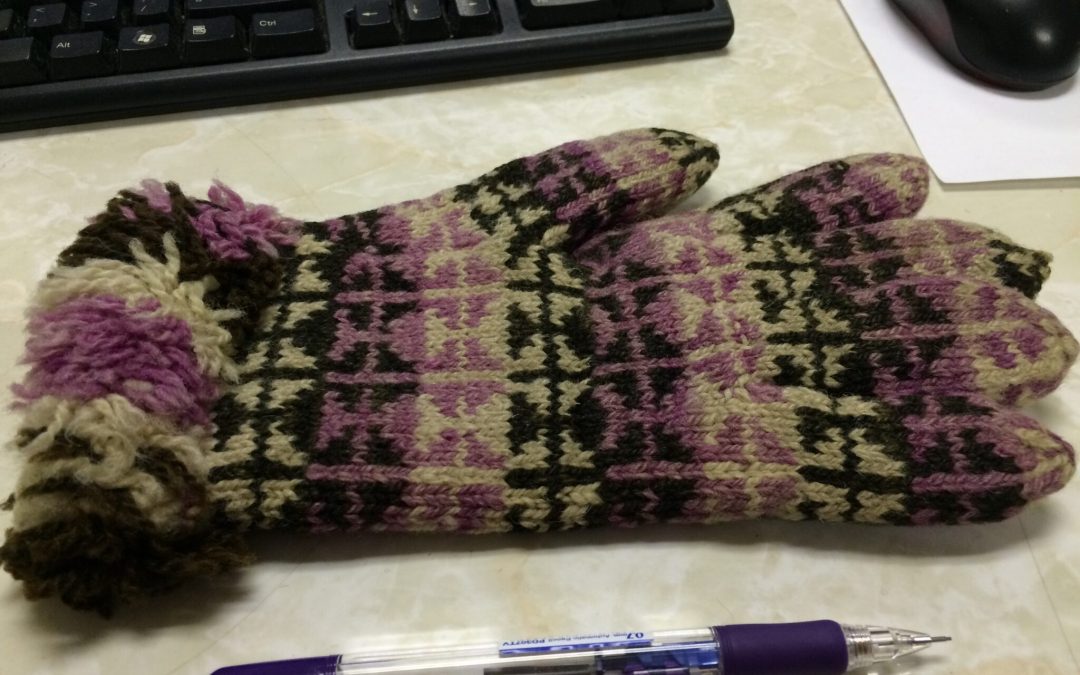
Guest blogger Sharlene Young-Bolen, of Stitch Revival Studio in Blyth, shares more about how a Huron County Museum artifact inspired her to create the Huron Wristers pattern and how her research into the origin of the pattern led her to connect to family of the original owner. Sharlene will be joining us March 25 when she will lead a virtual workshop to teach participants to make the Huron Wristers. The original gloves are currently on display in the Museum Gift Shop where Sharlene’s Huron Wristers kits are also available for purchase.

The knitted glove once owned by Herbert Wheeler.
The story of the creation of the Huron Wristers is a story of connections: the connection of past to present, of generation to generation.
Back in 1972, Pearl Wheeler donated a pair of knitted gloves that once belonged to her husband Herbert to the Huron County Museum and Historic Gaol. The museum’s record notes that at the time the gloves were thought to date from 1870 and were knit by a man.
Herbert and Pearl lived in Belgrave, ON. Herbert had seven siblings, four brothers and three sisters. His parents were Charles Wheeler and Mary Ann Wilkinson. Herbert was a carpenter and apparently also the local barber. How long the gloves were in Herb’s possession no one knows.
While visiting the museum to research women’s headcoverings – I had an idea to recreate a head scarf worn by one of my ancestors – I happened upon an image of Herb’s gloves. There was something very intriguing about the gloves. First, the colours – the pink is very bold and the contrast between the pink and black is quite striking. Secondly, the colourwork pattern – it seems familiar, but yet different somehow. It looks Fair Isle-inspired, but there’s something else there. And the fringe of the cuff, so interesting.

The Huron Wristers, inspired by the colourwork in Herbert’s knitted gloves.
Who made these gloves? There’s no record of that. The gloves may have been knitted for Herbert by an older family member; or purchased at some point earlier on and then Herbert inherited them; or Herbert bought the gloves himself from someone; or given his trade, perhaps they were payment for some work he did. It was time to do research on the pattern and see what could be found.
Herbert’s gloves were knit in the round using the stranded colourwork technique, working two colours of yarn in the same row, carrying the unused yarn across the inside of the work. The 8-stitch motif repeating pattern is similar to both the Shetland Fair Isle knitting pattern, ‘Little Flowers’ as well as an Estonian pattern called, ‘Cat’s Paw’.
The gloves feature a knitted fringe on a short ribbed cuff. Fringing has been used on both Latvian mittens and Estonian gloves, historical and modern versions and not so much in the Fair Isle tradition. The fringe appears to have been done using a loop technique which is done during the construction of the glove. The colourwork may seem close to the Sanquhar tradition, but it’s not a match for the following reasons according to knitters on the Knitting History Forum:
- There are quite a few designs associated with Sanquhar. Possibly the most well-known ones are based on 11 by 11 stitch squares. The squares have strong outlines with alternating patterns within the squares. Herb’s gloves therefore do not fulfill these criteria.
- Some Sanquhar gloves also have an interesting finger construction with little triangular gussets in the finger spaces and triangular finger tips. Also, all Sanquhar have a shaped thumb placed on the palm side rather than on the side of the hand as here.
- Finally, the stitch count, wool and colour are not really in the Sanquhar tradition. Gloves tend to be monochromatic. Wool used is finer, stitch count for the cuff around 80 stitches and modern needle size of around 2mm used.
The Knitting History Forum was invaluble as it connected me with Angharad Thomas, researcher, designer and knitter. Angharad wrote, “The only pattern I could find similar to that used in these gloves was a 4 stitch x 4 row triangle in a Shetland pattern book … but there’s a limit to what can be knitted on a given number of sts in whatever colours are to hand. That’s how I think these patterns came about rather than from one tradition or another. Fringes are now associated with Latvia but there are gloves from the north of England with a fringe…” Angharad then suggested I reach out to Shirley Scott, Canadian knitting designer and author.

Traditional Estonian gloves and mittens showing the beautiful colourwork and fringed cuffs.
Scott immediately suggested the similarity to Estonian mitten patterns and sent a few images of pattern motifs. She then pointed me in the direction of Nancy Bush, an Estonian knitting expert. Shirley also cautioned that there may be no clear and definitive answer as to the pattern name and origins.
“Don’t be surprised if the pattern has no real name. Newfoundland patterns have never had names, for example. We made ours up, as explained in our books. It’s also hard to pinpoint the origins of patterns these days because North America has had so many waves of immigration and so much pattern sharing,” said Scott.
Nancy Bush, a knitting writer, designer and authority on Estonian knitting, wrote:
“I have found a pattern close to the one on your mittens from both Paistu and Helme parishes in Estonia (these are southwest). The difference is that the diamond with cross shapes are offset, as is the example of Sander’s Mittens in Folk Knitting in Estonia. There is another pattern that is like the ones from Helme and Paistu in a pattern book from the Rannarootsi Museum in Haapsalu. This museum tells the story of Swedish/Estonian people who lived in Estonian territory, mostly until the 2nd WW. I don’t know the story of these exact mittens, just that the pattern is close.”

Estonian Mitten Pattern by Nancy Bush. The repeating motifs are almost a match for Herbert’s gloves, but for the fact they are offset, nested within each other, not point to point.
Bush continued, “The fact that the diamond with cross shapes are stacked instead of offset makes me think they were not looking at any of the patterns I have mentioned above, or mittens made like them…
All that being said… this is a very simple pattern, easy to create with knit stitches and could have originated almost anywhere… it is very possible these mittens were made by someone who was remembering a pattern they knew as a child, for instance, and reproduced it as best they could, with the yarn they had…”
So, which was it, Estonian or Fair Isle? It was time to research the Wheeler family and Herbert. Where did their family originate? Was there a family tie to either Estonia or the British Isles? When an instagram post by Best Dishes, a Goderich business owned by Sarah Anderson, appeared in my feed one day identifying the wristers pattern as based on a family heirloom, chance had dropped the opportunity in my lap. It was time to connect. A couple messages back and forth and the story unfolded…
Learn more:

by Amy Zoethout | Dec 24, 2020 | Archives, Artefacts, Blog, Exhibits
Technology over the last several years has made it so easy to quickly connect with friends and loved ones that the tradition of sending Christmas cards has not been as popular as it once was. But in the midst of a global pandemic, when we can’t celebrate together like we normally would, people are looking for more meaningful ways to let loved ones know they are thinking of them, and what better way than a lovely greeting delivered through the mail. And while we can’t send out a seasonal greeting to you all through the mail, we can still use the power of technology to share a little Christmas cheer by taking a look through some of the Christmas cards in our collection. 
Christmas Greetings, From Germany To Edith Williams From Prison Camp 106684 Co.10 Bar. B A994.0007.033

A Christmas notecard “Season’s Greetings”. On the front of card is a Tom Pritchard print of a farm/house by a hill and is signed by Tom Pritchard. Donated by Town of Goderich. 2011.0021.009


This Christmas postcard features flags of Allied nations in the First World War. The back of the card includes a bio of Ontario Premier William Hearst. 2004.0044.006

The back of this card has a silver embossed border. The front of the card is made of plastic with bells and holly designs on it. On the inside left is printed “THAT YOU’LL REMEMBER ME”. On the inside right is printed A GREETING…ANOTHER CHRISTMAS. A951.0664.001
 This Happy New Year postcard does not include a postmark, but reads on the back: “Dear cousin, received your cards yesterday and I was glad to hear from you’s. It is about 5 below zero, we have to go back to school next Monday. We have skating on Belles Isle. What did Santa Claus bring you for Christmas. Good bye from Harvey M Brien.” 2008.0032.005
This Happy New Year postcard does not include a postmark, but reads on the back: “Dear cousin, received your cards yesterday and I was glad to hear from you’s. It is about 5 below zero, we have to go back to school next Monday. We have skating on Belles Isle. What did Santa Claus bring you for Christmas. Good bye from Harvey M Brien.” 2008.0032.005
And, of course, we couldn’t share our Christmas card collection without sharing a selection of cards from artist Jack McLaren, who is the subject of our exhibit Reflections: The Life & Work of J.W. (Jack) McLaren. Depending on the year, his collection includes some happy and cheerful seasonal greetings….

And some that seem appropriate for the 2020 holiday season…









































